Delving into the Concept of Sacrifice and Offering in Roman Mythology
In Roman mythology, the act of sacrifice and offering played a significant role in religious practices and rituals. Let’s explore the foundational aspects of these acts and their importance within the context of Roman beliefs and traditions.
The Significance of Sacrifice in Roman Mythology
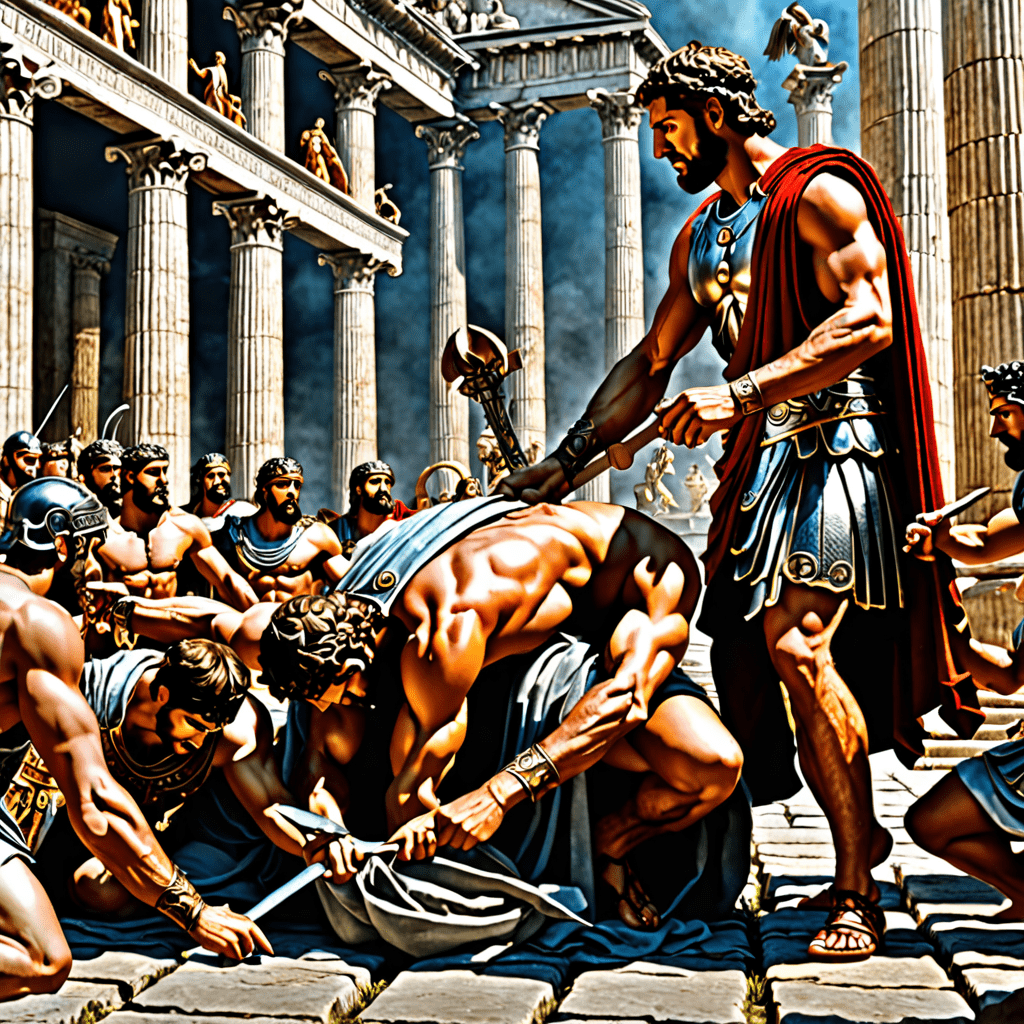
Sacrifice held a central place in Roman religious practices. Romans believed that offering sacrifices to their deities was crucial for maintaining harmony between humans and the gods. The act of sacrifice was seen as a way to communicate with the divine and seek favor, protection, or forgiveness.
Various types of sacrifices were conducted in Roman mythology, including animal sacrifices, libations (pouring of liquids), and offerings of crops or other goods. Each type of sacrifice was tailored to the specific deity being honored and the desired outcome.
Types of Offerings in Roman Mythology
Offerings in Roman mythology were not limited to sacrifices but included a wide range of items given to the gods as a sign of respect, gratitude, or supplication. These offerings could include fruits, flowers, incense, or valuable objects.
Additionally, Romans often presented votive offerings, which were objects dedicated to the gods as a pledge or in fulfillment of a vow. Votive offerings could range from small tokens to intricate sculptures, reflecting the personal devotion of the offeror.
The Rituals of Sacrifice and Offering
Rituals of sacrifice and offering in Roman mythology were highly structured and followed specific protocols. Priests, known as pontiffs, oversaw the ceremonies to ensure they were performed correctly and in accordance with religious customs.
The choice of animal for sacrifice, the manner of offering, and the accompanying prayers were all essential components of these rituals. The successful completion of a sacrifice or offering was believed to strengthen the bond between humans and the gods, ensuring divine favor and protection.
Legacy and Influence of Sacrifice and Offering
The legacy of sacrifice and offering in Roman mythology extends beyond ancient times, influencing modern practices and beliefs. Elements of Roman sacrificial rituals can still be seen in certain religious ceremonies and traditions around the world.
By understanding the concept of sacrifice and offering in Roman mythology, we gain insight into the religious mindset and spiritual practices of this ancient civilization. These acts served as a means of connection to the divine and a way to honor and appease the gods in the hopes of receiving their blessings.
FAQs About the Concept of Sacrifice and Offering in Roman Mythology
What was the significance of sacrifice in Roman mythology?
Sacrifice played a crucial role in Roman mythology as it was a way to communicate with the gods, seek their favor, and maintain harmony between the divine and mortal realms. It was believed that offerings appeased the deities and ensured prosperity, protection, and guidance for the community.
How were sacrifices and offerings performed in Roman mythology?
In Roman mythology, sacrifices and offerings were typically made at temples or altars dedicated to specific gods. Animals, crops, incense, and other valuable items were presented as gifts to the deities. Priests conducted elaborate rituals, including prayers and ceremonies, to ensure the offerings were acceptable and effective.
What types of sacrifices and offerings were common in Roman mythology?
Common types of sacrifices in Roman mythology included animal sacrifices, such as bulls, sheep, and pigs, which were often offered during major festivals and ceremonies. Additionally, offerings of wine, grain, and incense were made to honor the gods and seek their blessings for various aspects of life.
Why did Romans believe in the power of sacrifice and offering?
Romans believed that sacrifice and offering were essential for maintaining a harmonious relationship with the gods and ensuring divine favor and protection. By giving gifts to the deities, they sought to express