Slavic Mythology: The Art of Pottery and Ceramics
I. Origins and Historical Significance
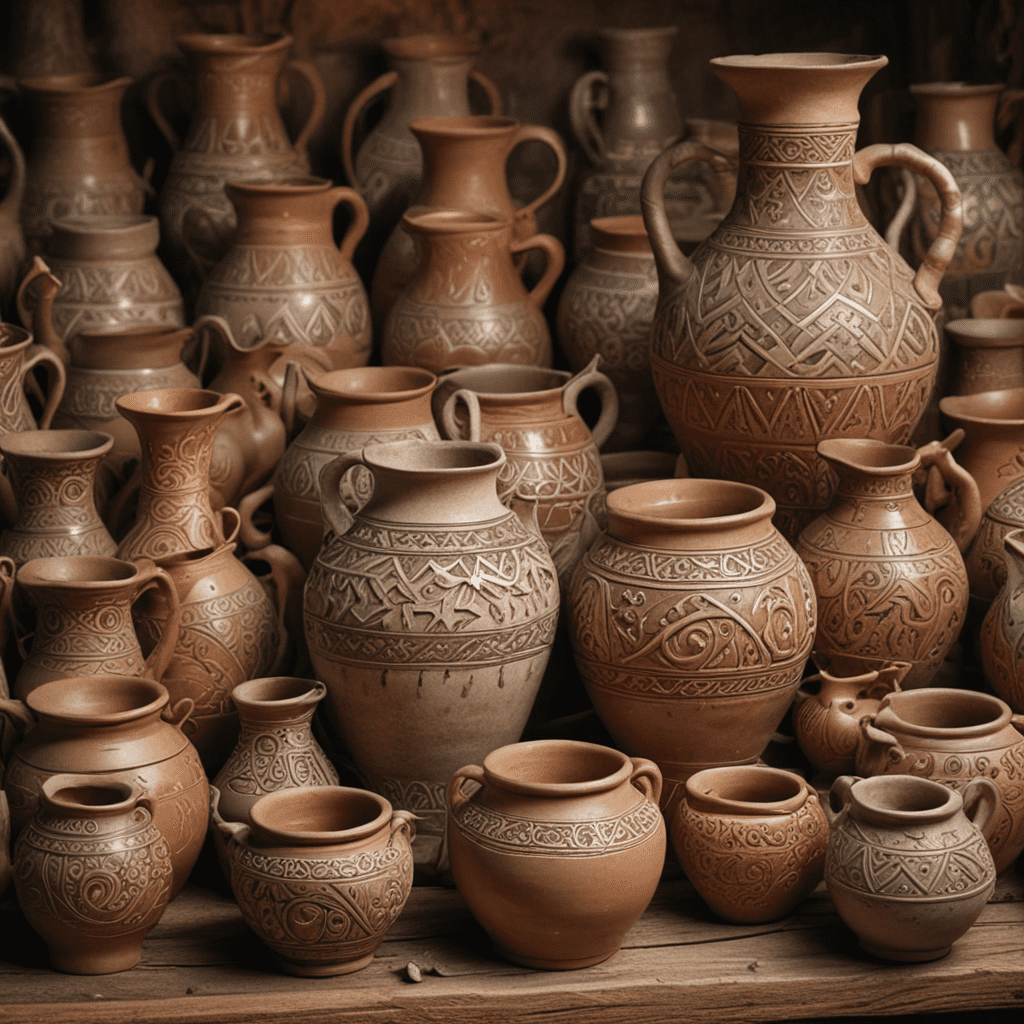
Slavic mythology holds a rich tapestry of beliefs and practices, and among its most notable traditions is the art of pottery and ceramics. The origins of Slavic pottery are deeply rooted in ancient history, with archaeological evidence indicating the production of earthenware vessels in Slavic lands as early as the 6th century BC. Over the centuries, Slavic pottery has evolved into a distinctive and cherished expression of cultural identity.
II. Symbolism and Beliefs
In Slavic mythology, pottery held immense symbolic value. It was believed that the creation of pottery vessels represented the cycle of life, death, and rebirth. The clay was seen as a symbol of Mother Earth, while the firing process represented the transformation of the vessel from its raw form into a durable and useful object. Pottery was also believed to possess protective powers, and was often used in rituals and ceremonies to ward off evil spirits.
III. The Role of the Potter in Slavic Society
In Slavic communities, potters held a respected and honored position. They were skilled artisans who possessed the knowledge and techniques to create both functional and decorative pottery. Potters were often considered to have a special connection to the supernatural world, and their work was revered for its beauty and its ability to connect with the divine.
IV. Techniques and Materials
Slavic pottery was primarily made using local clays, which varied in color and texture depending on the region. Potters employed various techniques to create their vessels, including hand-building, wheel-throwing, and mold-making. Hand-built pottery was created by shaping the clay by hand, while wheel-thrown pottery was formed on a rotating wheel. Mold-making involved pressing clay into a mold to create a desired shape.
V. Regional Variations
Slavic pottery exhibited regional variations in terms of style, decoration, and function. In some regions, such as Poland and Ukraine, pottery was characterized by intricate geometric patterns and bright colors. In other regions, such as Russia and Belarus, pottery tended to be more naturalistic and featured depictions of animals and plants.
VI. Pottery as a Symbol of Slavic Identity
Throughout history, Slavic pottery has served as a symbol of Slavic identity and cultural continuity. Pottery vessels were often decorated with traditional Slavic symbols and motifs, such as the sun, the moon, and the cross. In addition, pottery was used in traditional Slavic rituals and ceremonies, further cementing its significance within Slavic culture.
VII. The Art of Glazing
Glazing, the process of applying a vitreous coating to pottery, was introduced to Slavic lands in the 10th century. Glazes were used to enhance the durability and aesthetics of pottery vessels. Slavic potters experimented with a variety of glazes, including lead glazes, ash glazes, and salt glazes, each producing unique colors and effects.
VIII. Common Motifs and Designs
Slavic pottery often featured common motifs and designs that carried symbolic meanings. The sun, a symbol of fertility and life, was a popular motif, as were animals such as horses, birds, and wolves. Geometric patterns, such as spirals and meanders, were also commonly used, symbolizing the interconnectedness of all things.
IX. Contemporary Revival of Slavic Pottery
In recent years, there has been a growing revival of interest in Slavic pottery. Contemporary potters are drawing inspiration from traditional Slavic designs and techniques to create new and innovative works of art. This revival has helped to ensure the continuation of Slavic pottery as a vibrant and living tradition.
X. Cultural and Archaeological Significance
Slavic pottery holds immense cultural and archaeological significance. It provides valuable insights into the beliefs, practices, and artistic traditions of Slavic peoples throughout history. Archaeological excavations have uncovered a wealth of Slavic pottery, which has helped to piece together the story of Slavic culture and its evolution over time.
FAQs
Q: What is the oldest known example of Slavic pottery?
A: The oldest known example of Slavic pottery dates back to the 6th century BC and was discovered in Poland.
Q: What were the different techniques used to create Slavic pottery?
A: Slavic potters used hand-building, wheel-throwing, and mold-making to create their vessels.
Q: What materials were used to make Slavic pottery?
A: Slavic pottery was primarily made using local clays, which varied in color and texture depending on the region.
Q: What is the significance of Slavic pottery?
A: Slavic pottery holds immense cultural and archaeological significance, providing insights into the beliefs, practices, and artistic traditions of Slavic peoples throughout history.