The Ifrit and the Nature of Power: Exploring their Authority and Influence
I. Introduction
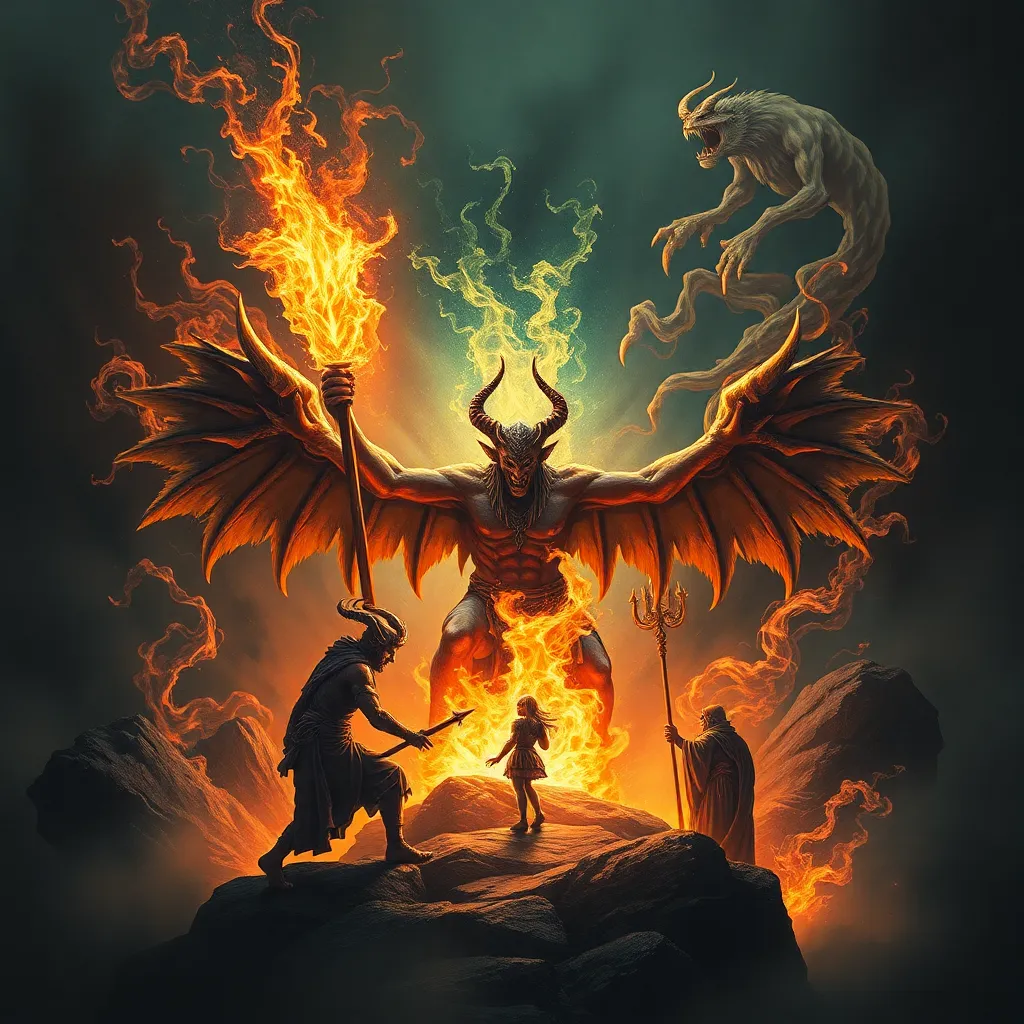
The Ifrit, a powerful supernatural being in Arabian mythology, is often depicted as a fiery creature with immense strength and cunning. In the context of folklore, the Ifrit embodies the complexities of power dynamics, representing both the allure and danger of unchecked authority.
This article aims to delve into the authority and influence of the Ifrit, exploring its origins, characteristics, and significance in various cultures. By examining the Ifrit’s role in mythology, we can gain insight into broader themes of power and control that resonate through human history.
II. Historical Context of the Ifrit
The Ifrit’s origins can be traced back to pre-Islamic Arabian culture, where it was often associated with fire and the desert, symbolizing both destruction and transformation. Over time, the Ifrit’s image has evolved, influenced by Islamic tradition and cultural exchanges across the Middle East and North Africa.
In various cultures, the Ifrit has been compared to other supernatural beings, such as:
- The jinn, with whom the Ifrit shares similarities but differs in strength and temperament.
- Demons from other mythologies, often embodying chaos and moral ambiguity.
This cultural evolution highlights the Ifrit’s adaptability as a symbol of power across different narratives and belief systems.
III. Characteristics of the Ifrit
Ifrits are commonly portrayed as large, imposing figures, often with features that suggest their fiery nature, such as:
- Brightly glowing eyes.
- Smoke or flames emanating from their bodies.
- Animalistic traits, such as horns or claws.
In literature and art, the Ifrit embodies various symbolic meanings, representing:
- The duality of creation and destruction.
- The struggle between human beings and the forces they cannot control.
The characteristics of the Ifrit signify a profound sense of authority, as they possess the ability to manipulate natural elements and alter the fate of individuals.
IV. The Role of Ifrit in Folklore and Legends
Ifrits appear in numerous stories and legends, with some key narratives including:
- The tale of The Fisherman and the Ifrit from *One Thousand and One Nights*, where a fisherman must outsmart an Ifrit to save himself.
- Stories of encounters with Ifrits that serve as cautionary tales about arrogance and greed.
These narratives often convey moral lessons, emphasizing the consequences of disturbing the balance of power. The Ifrit also serves as a metaphor for uncontrollable power, illustrating the dangers that arise when humans attempt to wield forces beyond their comprehension.
V. Authority and Influence of the Ifrit
The mechanisms of power exercised by Ifrits in myths often involve:
- Manipulation of fire and smoke, which symbolizes their raw, destructive power.
- Psychological influence over humans, inducing fear or temptation.
The relationship between Ifrit and humans is complex; while Ifrits can be malevolent, they may also offer boons or fulfill wishes, albeit with a high cost. This duality creates a tense dynamic where humans must navigate the fine line between respect and fear.
The psychological impact of the Ifrit’s influence is profound, as their presence often evokes themes of dread and fascination, prompting reflections on humanity’s relationship with power and the unknown.
VI. Comparative Analysis: Ifrit and Other Figures of Power
When comparing the Ifrit to other mythological beings, several notable differences emerge:
- Ifrits are often more chaotic and unpredictable than jinn, who are typically seen as more neutral.
- While demons are often bound to moral judgment, Ifrits embody a more primal form of power detached from human morality.
This cross-cultural interpretation of power reveals that the Ifrit, while unique, shares common themes with mythological figures worldwide. The modern portrayal of Ifrits often emphasizes their complexity, merging traditional views with contemporary narratives that explore themes of rebellion and authority.
VII. The Ifrit in Contemporary Culture
The Ifrit has found a place in modern media, appearing in various forms such as:
- Literature, where authors reinterpret the Ifrit’s characteristics to fit new narratives.
- Film, often representing Ifrits as antagonists or misunderstood beings.
- Video games, where players may encounter Ifrits as powerful foes or allies.
The continuing relevance of the Ifrit’s authority and influence speaks to the enduring fascination with power dynamics in human stories. As narratives evolve, the transformation of the Ifrit myth reflects contemporary societal issues and the complexities of authority in the modern world.
VIII. Conclusion
In summary, the Ifrit represents a fascinating intersection of power and influence within mythology. Through its rich historical context, distinctive characteristics, and significant role in folklore, the Ifrit embodies the complexities of authority in a way that resonates across cultures and eras.
Reflecting on the broader implications of authority in mythology, it becomes clear that the Ifrit serves as a reminder of the dual nature of power—its potential to create and destroy. Future studies of the Ifrit and similar entities in folklore may reveal even deeper insights into humanity’s ongoing relationship with power and the supernatural.