1. Introduction
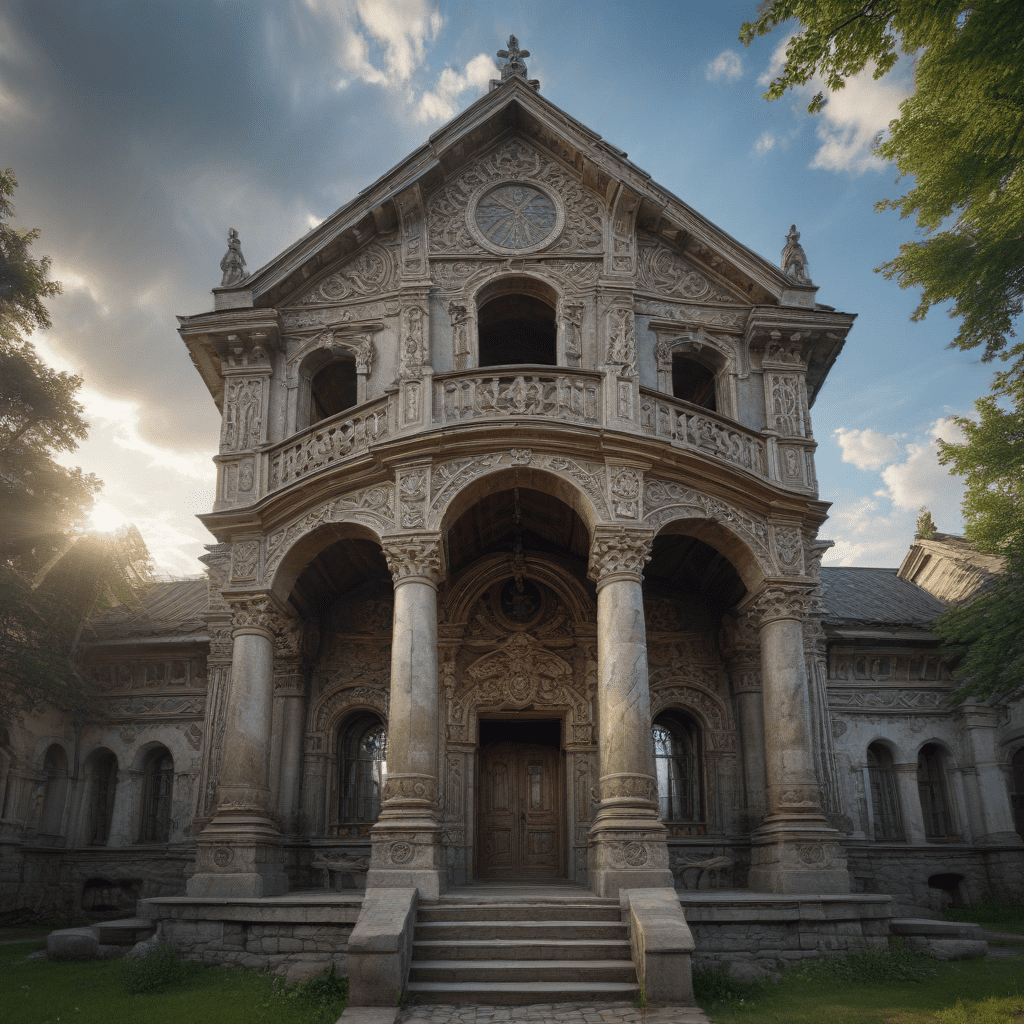
Slavic mythology, a rich tapestry of ancient beliefs and legends, has profoundly influenced the architectural traditions of Slavic cultures. Slavic architecture, deeply rooted in the spiritual and cultural beliefs of its people, showcases a unique blend of mythological symbolism, protective elements, and a deep connection to the natural world. This article explores the intricate relationship between Slavic mythology and traditional architecture, unraveling the ways in which folklore, beliefs, and rituals shaped the built environment across Slavic regions.
2. Historical Context
The origins of Slavic mythology date back to the early Slavic tribes who inhabited vast territories spanning Eastern Europe. Over centuries, these tribes developed a complex system of beliefs, deities, and rituals that influenced all aspects of their lives, including architecture. The rise of Christianity in the region did not completely eradicate these ancient beliefs; instead, they often intertwined with Christian traditions, giving rise to a syncretic blend of spiritual influences in architectural practices.
3. The Role of Spirits and Ancestors
Slavic mythology is populated by a vast array of spirits and supernatural beings, including house spirits, forest spirits, water spirits, and the spirits of ancestors. These beings were believed to have a profound impact on the well-being of individuals and communities, and thus, their presence was acknowledged and honored through architectural practices. Houses were designed with specific spaces and rituals dedicated to appeasing these spirits, ensuring harmony and protection.
4. The Influence of Natural Elements
Slavic mythology places great significance on the natural world, viewing it as a source of both sustenance and spiritual power. Forests, rivers, and mountains were considered sacred, and their presence influenced architectural design. Buildings were often constructed using natural materials such as wood and stone, reflecting the close relationship between humans and their surroundings. Orientation and placement of structures were also influenced by the perceived alignment with natural forces and the cycles of nature.
5. Traditional Rituals and Architecture
Traditional Slavic rituals played a crucial role in shaping architectural practices. Rituals associated with birth, marriage, death, and seasonal celebrations were often performed within specific architectural spaces, such as temples or sacred groves. These spaces were designed to facilitate communication with the divine, honor ancestors, and mark important life events. By incorporating ritualistic practices into architecture, Slavic cultures created a built environment that was deeply connected to their spiritual and cultural traditions.
6. Slavic Mythology in Building Materials
Slavic mythology also manifested in the choice of building materials. Wood, considered a living and sacred material, was widely used in Slavic architecture. Trees were seen as intermediaries between the human and divine realms, and their wood was believed to possess protective properties. Stones, too, were imbued with symbolic meanings and were incorporated into architectural designs as symbols of strength, longevity, and cosmic order. The careful selection and use of building materials reflected the spiritual significance attached to the construction process.
7. Symbolism and Ornamentation
Slavic mythology deeply influenced the symbolism and ornamentation found in traditional architecture. Geometric patterns, such as circles, squares, and crosses, were often used to represent the elements, celestial bodies, and divine beings. Animal motifs, including birds, horses, and bears, symbolized power, fertility, and protection. These symbols were incorporated into carvings, paintings, and other decorative elements, adorning both exterior and interior spaces and imbuing buildings with spiritual and protective significance.
8. Protective and Apotropaic Features
славянская мифология played a significant role in shaping protective and apotropaic features in Slavic architecture. Buildings were often adorned with symbols and amulets believed to ward off evil spirits, bring good luck, and protect the inhabitants from harm. Horse-shaped weathervanes were placed atop roofs to protect against lightning strikes, while garlic and onion braids were hung in doorways to keep out malevolent spirits. These protective elements were integral to Slavic architecture, reflecting the belief in the constant presence of supernatural forces and the need to safeguard against them.
9. The Impact on Settlement Patterns
Slavic mythology not only influenced the design of individual buildings but also shaped settlement patterns. Villages were often organized around central sacred sites, such as temples or groves, which served as spiritual and communal hubs. Slavic communities also believed in the significance of natural landmarks, such as rivers, hills, and forests, and often chose to settle near these places, considering them to be imbued with supernatural powers. These beliefs played a significant role in determining the location, orientation, and layout of Slavic settlements.
10. Contemporary Interpretations
In contemporary times, there is a renewed interest in Slavic mythology and its influence on traditional architecture. Many modern architects and designers incorporate elements inspired by Slavic folklore into their work. They explore the use of natural materials, traditional symbols, and protective features to create buildings that resonate with the cultural heritage and spiritual sensibilities of Slavic people. This contemporary interpretation of Slavic mythology in architecture not only preserves cultural traditions but also fosters a connection to the rich mythical and spiritual legacy of the Slavic ancestors.
FAQs
Q1. How did Slavic mythology influence the choice of building materials?
A. Slavic mythology considered wood and stones as sacred materials with symbolic meanings. Wood, seen as a living entity, possessed protective qualities, while stones represented strength and cosmic order. These materials played a significant role in the construction of Slavic buildings.
Q2. What role did symbolism play in Slavic architecture?
A. Slavic mythology influenced various symbolic motifs incorporated into architecture. Geometric patterns represented elements and celestial bodies, while animal motifs symbolized power, fertility, and protection. These symbols were used as decorative elements, imbuing buildings with spiritual significance.
Q3. Did Slavic mythology impact the layout of settlements?
A. Yes, Slavic mythology played a role in shaping settlement patterns. Villages were organized around central sacred sites, considering natural landmarks as places with supernatural powers. The location, orientation, and layout of Slavic settlements were influenced by these beliefs.