The Underworld in Greek Mythology
What is the Underworld in Greek Mythology?
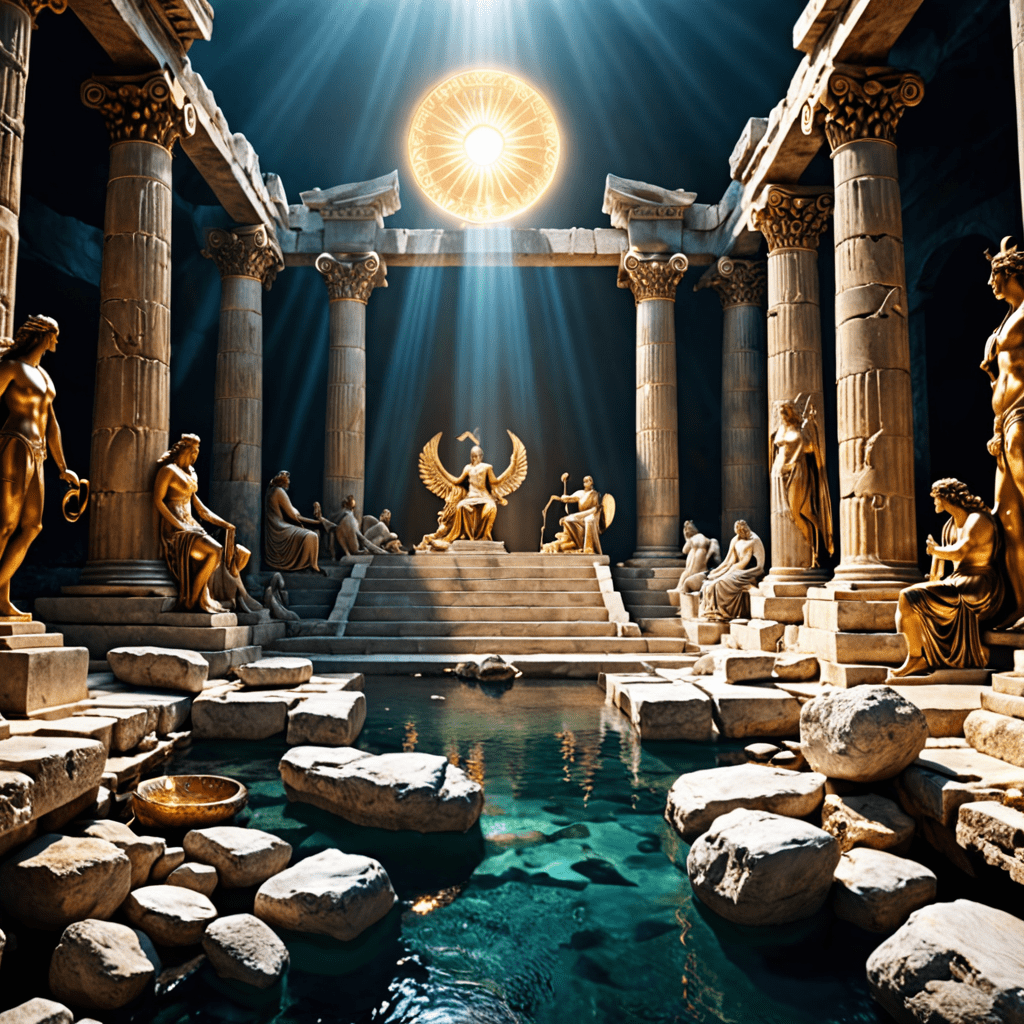
In Greek mythology, the Underworld is the realm that serves as the residence of the dead. It is ruled by Hades, the god of the Underworld, and is often referred to as the domain of shadows. The Underworld is a place where souls go after death to be judged and assigned to different afterlife destinations based on their deeds during their earthly lives.
Key Figures in the Underworld
One of the prominent figures in the Greek Underworld is Hades, the god who governs the realm alongside his wife, Persephone. Charon, the ferryman, is tasked with transporting the souls of the deceased across the River Styx to the afterlife. Cerberus, the three-headed dog, guards the gates of the Underworld, ensuring that the dead do not escape and the living do not trespass.
Realms of the Underworld
The Greek Underworld is divided into several regions, including the Asphodel Meadows where ordinary souls wander aimlessly, the Elysian Fields reserved for the virtuous and heroic souls, and Tartarus, a deep abyss where the wicked are condemned to suffer for eternity. Each realm serves a specific purpose in the afterlife judgment process.
Mythological Stories of the Underworld
Many Greek myths involve journeys to the Underworld, such as Orpheus’ quest to retrieve his beloved Eurydice, and Persephone’s cyclical abduction and return from the realm of the dead. These stories provide insights into the Greek beliefs about death, the afterlife, and the consequences of one’s actions in both life and death.
FAQs about The Underworld in Greek Mythology
What is the Underworld in Greek Mythology?
The Underworld in Greek Mythology is the realm of the dead, ruled by Hades. It is where souls go after death to be judged and assigned to their afterlife. It is a place of darkness and shadows, where the River Styx and other mythical elements are believed to exist.
Who rules the Underworld in Greek Mythology?
The Underworld is ruled by Hades, the god of the underworld and wealth. He is one of the three major Olympian gods, along with his brothers Zeus and Poseidon. Hades is responsible for overseeing the souls of the deceased and maintaining order in the Underworld.
What are some key features of the Underworld in Greek Mythology?
The Underworld is home to various regions such as the Fields of Punishment, Elysium, and the Asphodel Meadows. It also houses significant landmarks like the palace of Hades, the River Styx, and the judges of the dead. Cerberus, the three-headed dog, guards the gates of the Underworld to prevent the living from entering.