Beyond the Myth: The Peryton in Roman Literature and Philosophy
I. Introduction
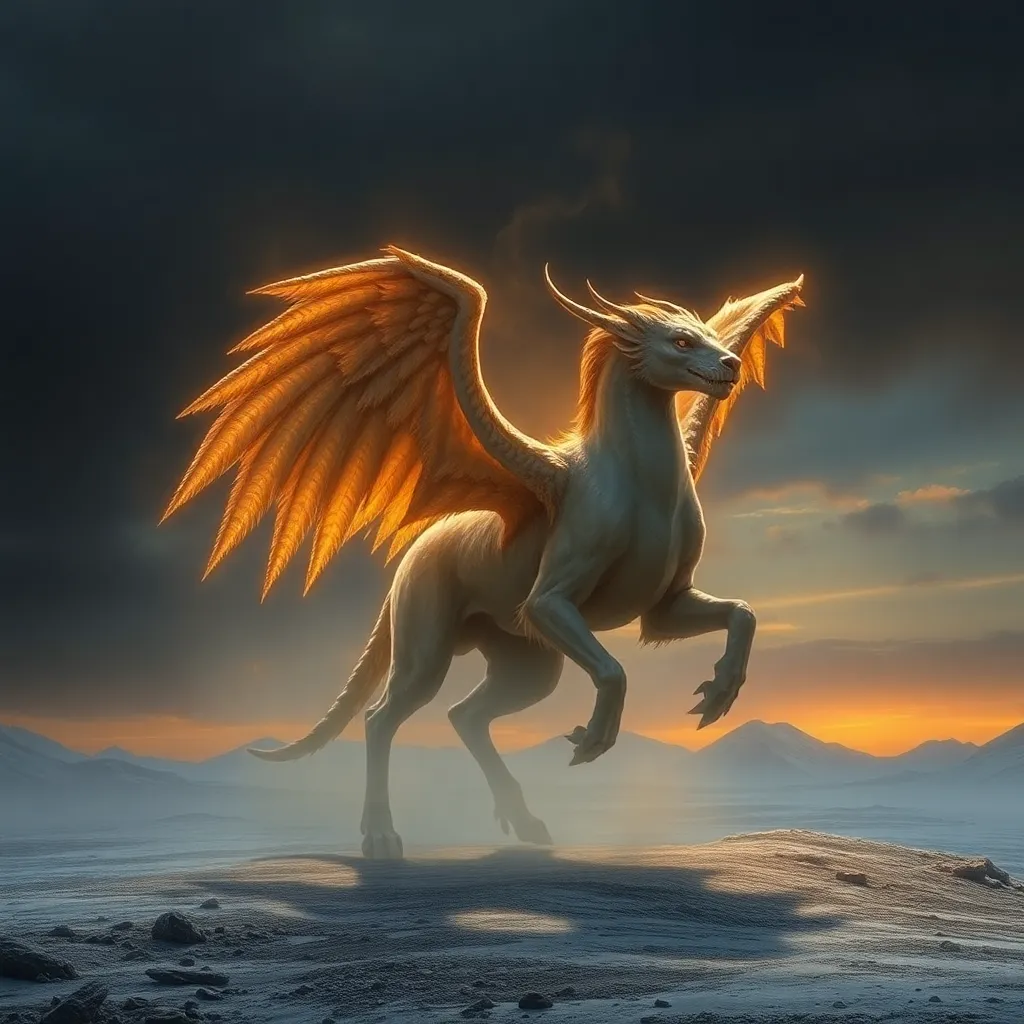
The Peryton is a fascinating mythical creature often depicted as a winged animal with the body of a deer and the head of a bird. This unique amalgamation of features gives the Peryton a striking appearance, allowing it to capture the imagination of those who encounter it in various forms of literature and art.
In Roman culture, the Peryton served not only as a creature of myth but also as a symbol of deeper philosophical and moral themes. Its significance can be traced through historical texts, literature, and evolving interpretations that reflect the complexities of human experience and understanding.
This article aims to explore the various facets of the Peryton, delving into its historical context, literary representations, philosophical interpretations, symbolic meanings, artistic depictions, and its legacy in modern culture.
II. Historical Context of the Peryton
A. Origins of the Peryton myth in ancient texts
The origins of the Peryton can be found in ancient texts where it is often mentioned in conjunction with other mythical beings. Roman writers and poets utilized the Peryton to illustrate themes of transformation, duality, and the natural world.
B. Comparisons to other mythical creatures in Roman mythology
When examining the Peryton, it is helpful to compare it with other mythical creatures of Roman mythology. For instance:
- The Chimera: A fire-breathing monster composed of parts from various animals.
- The Griffin: A regal creature with the body of a lion and the head of an eagle, symbolizing strength and wisdom.
- The Sphinx: A creature with a human head and a lion’s body, known for its riddles and mysteries.
These comparisons highlight the Peryton’s unique characteristics while underscoring the Roman fascination with hybrid creatures that embody multiple aspects of nature.
C. The role of the Peryton in Roman folklore
In Roman folklore, the Peryton was often portrayed as a guardian of the forest, embodying the spirit of nature and wilderness. Its elusive nature made it a subject of many tales, where it represented the unknown and the mystical aspects of the world.
III. The Peryton in Roman Literature
A. Analysis of key literary works featuring the Peryton
Several key works of Roman literature feature the Peryton, serving as a vehicle for exploring complex themes. Notable examples include:
- Ovid’s Metamorphoses: The Peryton appears in tales that focus on transformation, highlighting its dual nature.
- Virgil’s Aeneid: The creature serves as a metaphor for the struggles faced by the protagonist, representing the tension between man and nature.
B. Symbolism and themes associated with the Peryton in literature
The Peryton is often associated with themes of:
- Transformation: Reflecting the potential for change and growth.
- Duality: Representing the conflict between human desires and natural instincts.
- Freedom: Symbolizing the yearning for liberation from societal constraints.
C. Influence of the Peryton on Roman storytelling traditions
The Peryton’s unique characteristics and symbolism influenced Roman storytelling traditions by providing authors with a rich source of inspiration. Its presence in narratives often encouraged deeper reflections on the human condition and the relationship between humanity and the natural world.
IV. Philosophical Interpretations of the Peryton
A. Philosophers’ perspectives on myth and reality
Philosophers in Roman times often debated the nature of myths and their relation to reality. The Peryton, as a mythical creature, served as a subject for discussions about the boundaries between the real and the imagined.
B. The Peryton as a subject of allegorical analysis
Many philosophers viewed the Peryton allegorically, interpreting its physical form as a representation of the human psyche. The creature’s dual nature prompted discussions about:
- The conflict between reason and emotion.
- The struggle for self-identity.
- The search for meaning in a chaotic world.
C. The Peryton in the context of moral and ethical discussions
The Peryton also entered moral and ethical discussions, often symbolizing the consequences of human ambition and desire. Its mythical status allowed philosophers to explore themes of virtue, vice, and the human experience in a nuanced manner.
V. The Peryton and Its Symbolic Meanings
A. Exploration of the Peryton as a symbol of transformation
At its core, the Peryton represents transformation—an emblem of change and adaptability. This symbolism resonates with the human experience, where transformation is a constant theme in life.
B. Connections between the Peryton and concepts of the sublime
The Peryton’s majestic form evokes feelings of the sublime, where beauty and terror coexist. This connection allows for explorations of the limits of human understanding and the awe-inspiring aspects of nature.
C. The Peryton’s role in representing human fears and aspirations
Furthermore, the Peryton embodies human fears and aspirations, serving as a reminder of the duality of existence. It highlights the tension between our desires for freedom and the constraints imposed by society.
VI. The Peryton in Art and Iconography
A. Depictions of the Peryton in Roman art and sculpture
The Peryton has been depicted in various forms of Roman art and sculpture, often rendered with intricate details that emphasize its unique features. These artistic representations serve to immortalize the creature in the cultural memory of Rome.
B. The influence of the Peryton on later artistic movements
Throughout history, the influence of the Peryton can be seen in various artistic movements, including the Renaissance and Romanticism, where artists sought to capture the essence of mythical creatures and their symbolic meanings.
C. Visual interpretations and their meanings
Visual interpretations of the Peryton often emphasize its ethereal qualities, reflecting the dual nature of beauty and danger. These representations invite viewers to engage with the deeper meanings behind the creature’s symbolism.
VII. The Legacy of the Peryton in Modern Culture
A. The resurgence of interest in the Peryton in contemporary literature
In recent years, there has been a resurgence of interest in the Peryton within contemporary literature. Modern authors draw upon its rich symbolism to explore themes of identity, transformation, and the relationship between humanity and nature.
B. Adaptations and representations in modern media
The Peryton has also found its way into various forms of modern media, including:
- Films: Where it often symbolizes the clash between nature and civilization.
- Video games: Featuring the Peryton as a mystical creature that players encounter in fantastical realms.
C. The Peryton as a cultural symbol in the 21st century
Today, the Peryton stands as a cultural symbol, embodying the complexities of human experience and the ongoing exploration of myth in understanding our world. Its presence in contemporary narratives serves as a reminder of the enduring power of myth and its relevance to modern life.
VIII. Conclusion
A. Summary of key points discussed
This article has explored the Peryton’s multifaceted role in Roman literature and philosophy, tracing its origins, literary significance, philosophical interpretations, symbolic meanings, artistic representations, and its legacy in modern culture.
B. Reflection on the enduring impact of the Peryton in literature and philosophy
The Peryton continues to resonate within the realms of literature and philosophy, serving as a bridge between ancient myths and contemporary understanding. Its ability to encapsulate complex themes makes it a timeless subject for exploration.
C. Final thoughts on the relevance of myth in understanding human experience
Ultimately, the Peryton reminds us of the power of myth in shaping our understanding of the human experience. Through its rich symbolism and narrative potential, the Peryton invites us to reflect on our own transformations, aspirations, and fears in a world that is continuously evolving.