Guardians of the Mines: Delving into Dwarf Mythology in the Tolkien Universe
I. Introduction to Dwarf Mythology in Tolkien’s Works
J.R.R. Tolkien is often celebrated as the father of modern fantasy literature, having created a rich and expansive universe that has influenced countless authors and creators. Among the many races that inhabit his Middle-earth legendarium, Dwarves hold a unique and significant place. Known for their resilience, craftsmanship, and deep connection to the earth, Dwarves embody themes of loyalty, honor, and the importance of heritage.
This article aims to explore the mythology of Dwarves within Tolkien’s works, examining their origins, societal roles, craftsmanship, relationships with other races, and their enduring legacy in popular culture.
II. Origins of the Dwarves: A Creation Myth
The creation of the Dwarves is attributed to Aulë, one of the Valar, who was inspired to create beings that could appreciate and work with the earth’s materials. According to Tolkien’s lore, Aulë fashioned the Dwarves from stone and earth, imbuing them with a love for craftsmanship and mining.
The significance of craftsmanship in Dwarf culture cannot be overstated. Dwarves are not merely miners but also master artisans, with a profound respect for labor and the fruits of their work. This creative drive echoes through their stories and songs, highlighting their identity as builders and creators.
When compared to other mythological creation stories, such as the creation of humanity in various cultures, the Dwarven origin story emphasizes the importance of skill and craftsmanship, rather than mere existence. This unique angle provides a deeper understanding of their character.
III. The Role of Dwarves in Middle-earth
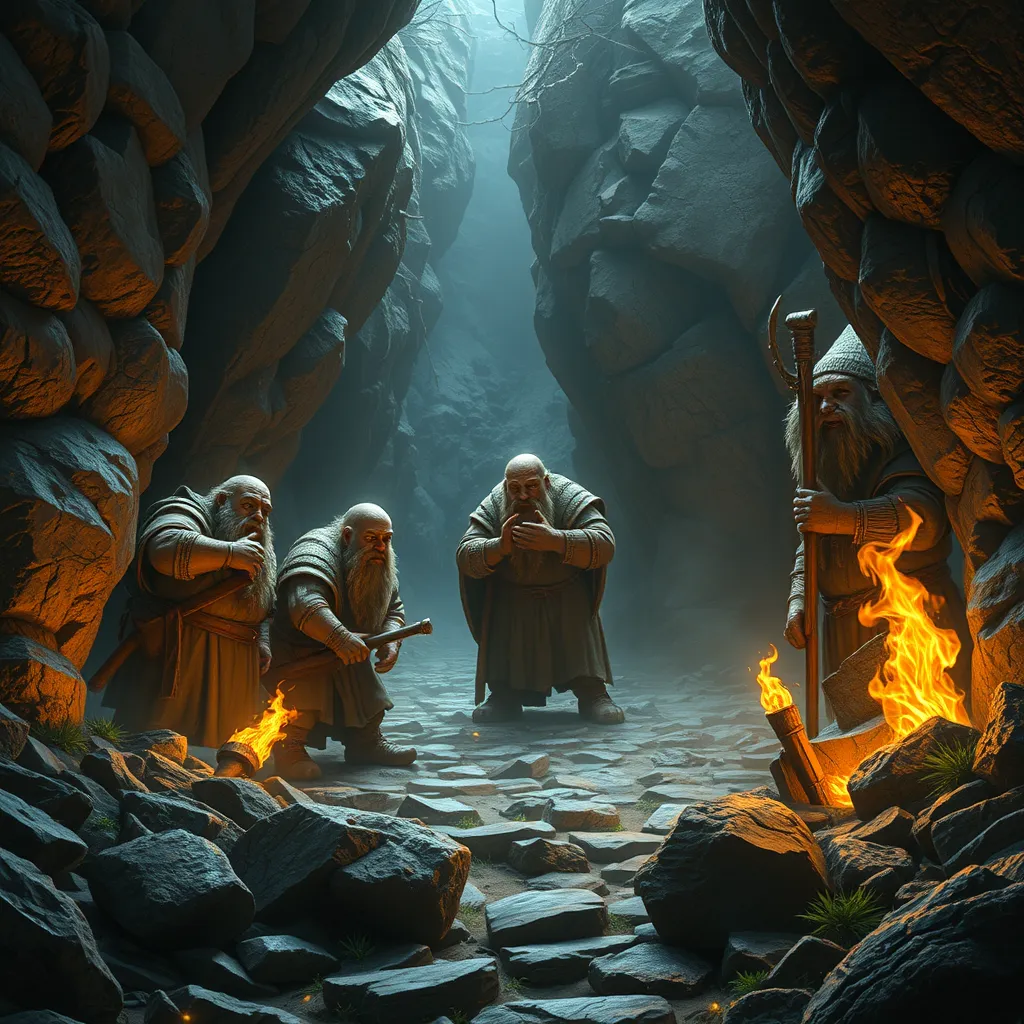
Dwarves are portrayed as the guardians of the earth and its treasures, often depicted as protectors of ancient secrets and riches hidden deep within the mountains. Their societies are structured around clans, each with its own history and traditions, such as the Durin’s Folk, who are central to the narrative of “The Hobbit” and “The Lord of the Rings.”
Key Dwarf characters, such as Thorin Oakenshield, Gimli, and Balin, contribute significantly to the overarching narratives of Tolkien’s works. Their quests and struggles highlight themes of bravery, loyalty, and the unyielding spirit of the Dwarves.
- Thorin Oakenshield: Leader of the Company of Dwarves in “The Hobbit,” he seeks to reclaim the Lonely Mountain and its treasure.
- Gimli: A member of the Fellowship of the Ring, representing Dwarves in the struggle against Sauron.
- Balin: A noble Dwarf who seeks to reclaim Moria, illustrating the Dwarven desire for heritage and home.
IV. The Significance of Dwarven Craftsmanship
Dwarven craftsmanship is legendary in Middle-earth, characterized by their mastery of mining and metallurgy. They are renowned for creating some of the most powerful artifacts, such as:
- Narsil: The sword of Elendil, broken during the Last Alliance of Elves and Men.
- The Arkenstone: A precious gem of unmatched beauty, considered the heart of the mountain by Thorin and his kin.
The cultural implications of this craftsmanship extend beyond mere utility; it serves as a representation of identity, pride, and the Dwarves’ relationship with the earth. Their works reflect their values of hard work, tradition, and the pursuit of excellence, establishing a legacy that resonates throughout Middle-earth.
V. Dwarven Relationships with Other Races
The interactions between Dwarves and other races—Elves, Men, and Hobbits—are marked by a complex history of both conflict and cooperation. Historically, Dwarves had a fraught relationship with Elves, stemming from misunderstandings and competition over precious resources. However, alliances have also formed, as seen in various narratives.
Some key points regarding these interactions include:
- Conflicts over treasures and territory, particularly with Elves over the Silmarils and the treasures of Moria.
- Alliances formed during battles against common foes, such as Sauron.
- The unique camaraderie developed with Hobbits, particularly through characters like Gimli and his friendship with Legolas.
These relationships add depth to Dwarf mythology, showcasing their resilience and adaptability in the face of adversity.
VI. The Dwarven Afterlife: Beliefs and Traditions
Dwarven beliefs regarding death and the afterlife are steeped in tradition. They view death not as an end but as a transition, with a strong belief in the honor of the ancestors. Dwarven burial practices reflect their respect for the dead, often involving elaborate tombs filled with items of significance.
Significant aspects of Dwarven death traditions include:
- Tombs: Lavish burial sites, often carved into mountains, serving as a testament to the deceased’s legacy.
- Celebration of Ancestors: Dwarves honor their ancestors through stories, songs, and rituals, ensuring their memories live on.
- Mythology of Spirits: Dwarven spirits are thought to linger in their ancestral halls, guiding and protecting their descendants.
VII. Dwarves in Popular Culture: Legacy of Tolkien’s Creation
The portrayal of Dwarves in adaptations of Tolkien’s works, such as Peter Jackson’s film trilogies, has cemented their place in popular culture. While the films brought Dwarves to a wider audience, they also introduced new interpretations and visual representations that differ from the original texts.
When comparing Tolkien’s Dwarven mythology to other fantasy representations, several similarities and differences emerge:
- Similarities: Dwarves are often depicted as stout, hardy beings with a love for mining and treasure.
- Differences: Other fantasy works may portray Dwarves as less complex, reducing them to mere comic relief rather than the noble, multifaceted characters found in Tolkien’s writings.
The ongoing influence of Tolkien’s Dwarven mythology is evident in various media, inspiring countless adaptations, games, and literature that continue to build upon his legacy.
VIII. Conclusion: The Enduring Appeal of Dwarven Mythology
In summary, the exploration of Dwarven mythology in Tolkien’s works reveals key themes of creation, craftsmanship, relationships, and cultural identity. Dwarves serve as a vital component of the broader tapestry of mythology that enriches Middle-earth.
The significance of Dwarves extends beyond Tolkien’s universe, influencing modern fantasy and cultural representations. Their enduring appeal lies in their complex characterizations, values, and the rich, mythological narratives that surround them.
Ultimately, the legacy of Dwarven mythology continues to resonate, inviting both new and longtime fans to delve into the depths of their stories and the rich world Tolkien has created.