Pele: Hawaiian Goddess of Fire and Volcanoes
In the heart of the Pacific Ocean lies the archipelago of Hawaii, a land of breathtaking beauty and volcanic power. Here, in the rich tapestry of Hawaiian mythology, reigns Pele, the fiery goddess of volcanoes, whose legend has captivated generations. Pele's story is woven into the very fabric of Hawaiian culture, shaping the beliefs, rituals, and understanding of the islands' inhabitants.
Pele’s Origins and Ancestry
Pele's lineage can be traced back to the realm of the gods, her origins shrouded in ancient tales passed down through generations. She is said to be the daughter of Haumea, the goddess of fertility and childbirth, and Kane Milohai, the god of creation. Pele's siblings include Hiʻiaka, the goddess of healing and magic, and Kāne Milohai, the god of creation. Pele's family played a significant role in shaping the landscape and culture of the Hawaiian islands.
Pele’s Journey to Hawaii
Pele's story begins in the mythical island of Kahiki, a paradise far beyond the reach of human explorers. According to legend, Pele was banished from Kahiki for her fiery temper and destructive tendencies. Seeking refuge, she embarked on a perilous journey across the vast Pacific Ocean, carrying with her the sacred fire of her ancestors.
Pele's arrival in Hawaii is marked by dramatic volcanic eruptions, signifying the power she wielded. The islands, with their fiery hearts, became her domain, a testament to her extraordinary power over the forces of nature.
Pele’s Powers and Abilities
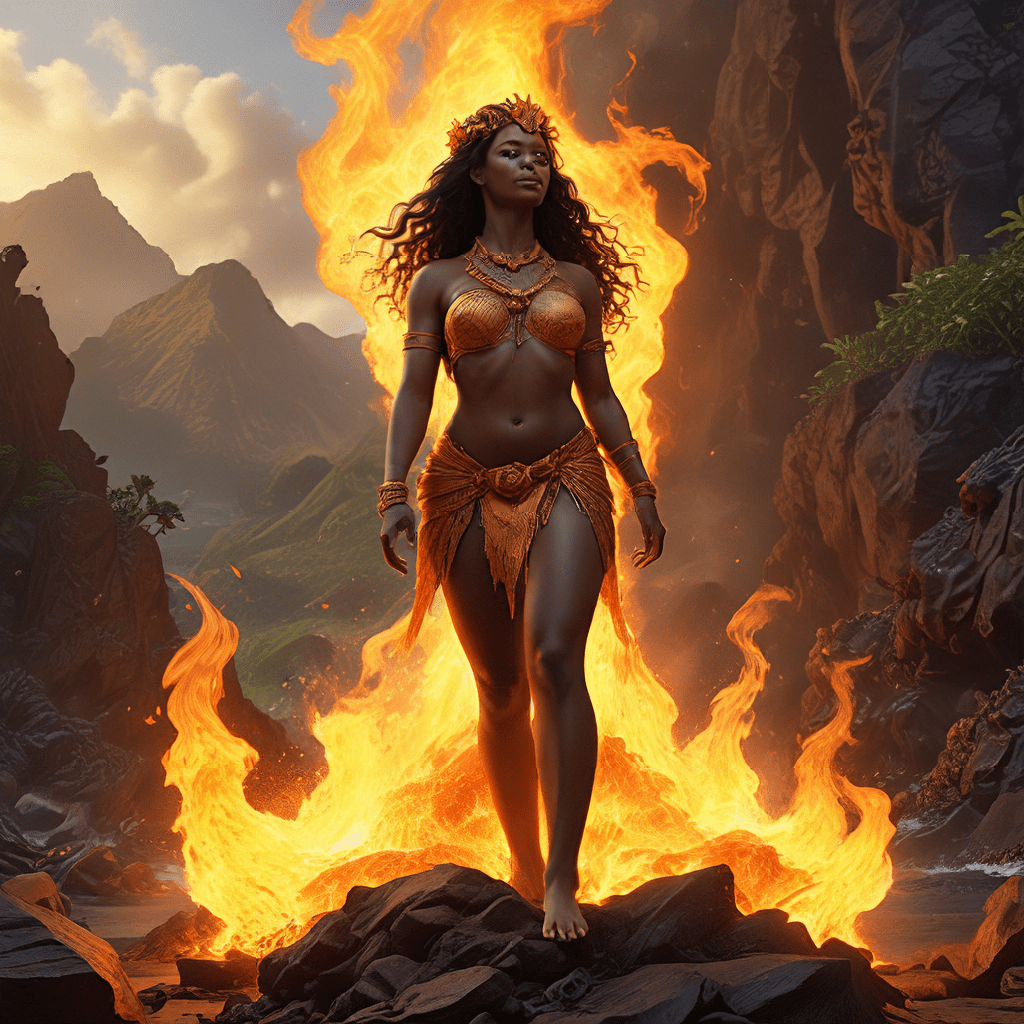
Pele's most notable attribute is her dominion over fire and volcanoes. Legend has it that she possessed the power to control molten lava, shaping the landscape with her fiery touch. She could summon volcanic eruptions, create fissures in the earth, and unleash fiery rivers of lava. Her volcanic creations were a source of both awe and fear, reminding the islanders of her immense power.
Pele's powers extended beyond volcanism. She was also associated with magic, healing, and prophecy. Her abilities reflected the complexities of the natural world, inspiring fear, respect, and reverence among the Hawaiian people.
Pele’s Volcanic Manifestations
Pele's legacy is indelibly etched in the landscape of Hawaii. From the towering summits of Mauna Kea and Mauna Loa to the volcanic craters and lava flows that dot the islands, her presence is felt throughout the archipelago. Each volcanic eruption, each flow of lava, is a testament to her enduring power.
Pele's volcanic creations are not just geological formations but symbols of her divine presence. Her power is a reminder of the forces that shape the world and the respect that is due to the natural order.
Pele’s Relationships and Family
Pele's relationships were as complex and fiery as her volcanic power. She was known for her passionate nature and her fierce protectiveness of her home, the Hawaiian islands. Her most famous relationship was with her younger sister, Hiʻiaka, the goddess of healing and magic. Hiʻiaka was a powerful goddess in her own right, and her relationship with Pele was a source of both love and conflict.
One of the most famous tales featuring Hiʻiaka tells of her journey to retrieve a sacred feather cloak for Pele. During this journey, Hiʻiaka met a young chief named Lohiau, and they fell in love. This caused Pele to become jealous, as she had desires for Lohiau herself. In her jealousy, Pele sent fiery lava flows to destroy Lohiau. Despite her sister's pleas, Pele refused to relent. However, Hiʻiaka, with her own magical powers, saved Lohiau from the lava's wrath. Ultimately, Pele allowed the couple to marry, but the episode illustrates the intensity of Pele's jealousy and her fierce control over her domain.
Beyond Hiʻiaka, Pele had other relationships with different gods and demigods. She was known to have affairs with mortals, and her children by these unions played a role in Hawaiian mythology. These relationships further illustrate Pele's complex character, emphasizing her human qualities alongside her divine powers.
Pele’s Jealousy and Wrath
Pele's fiery nature and volcanic abilities were often fueled by her jealousy, a theme that runs through many of her stories. She is portrayed as a possessive and powerful deity, fiercely guarding her domain and her lovers.
One of the most well-known examples of Pele's wrath involves the island of Kauaʻi. According to legend, Pele was vying for the affections of a handsome chief from Kauaʻi. However, the chief chose another woman, sparking Pele's intense jealousy. In a rage, Pele unleashed her volcanic fury upon Kauaʻi, causing widespread destruction. The island was left scarred by the eruption, a permanent reminder of Pele's vengeful power.
Pele's jealousy and wrath were not limited to mortals. She also displayed her rage against other deities, particularly those who dared to encroach on her domain. These conflicts often involved fierce battles fought with fire and magic, shaping the landscape of the Hawaiian islands and impacting the lives of the people.
Pele’s Role in Hawaiian Culture
Pele's legacy extends far beyond the realm of mythology. She plays a vital role in shaping the culture, beliefs, and practices of the Hawaiian people. Her presence is deeply ingrained in their understanding of the natural world, the volcanic forces that shape their islands, and the spiritual realm that connects them to the past.
The Hawaiian people developed rituals and offerings to appease Pele and seek her favor. These included offerings of food, flowers, and prayer, placed at the edges of volcanic craters or offered through the smoke of sacred fires. They believe that respecting Pele's power brings blessings, while disrespecting her can incur her wrath.
Pele’s legend continues to inspire art, music, and storytelling in Hawaiian culture. Her image appears in carvings, paintings, and traditional dances, reminding the people of their connection to the fiery goddess and the volcanic power that shapes their islands.
Legends of Pele’s Encounters
The stories of Pele's encounters with humans and other deities are rich and varied, reflecting the complex relationship between the divine and the mortal world. These tales are passed down through generations, offering insights into Hawaiian beliefs, values, and cultural practices.
One intriguing legend tells of a young Hawaiian woman who was captured by Pele's fiery wrath. She was trapped in a lava flow, but through her courage and determination, she was able to escape. This story highlights the resilience of the human spirit and the power of faith in the face of danger.
Another legend relates to a group of travelers who were caught in a volcanic eruption. Fearing for their lives, they made offerings to Pele, seeking her protection. Pele, moved by their devotion, spared their lives and guided them to safety. This story emphasizes the importance of respect and reverence towards the divine, and the power of humility in the face of overwhelming forces.
Theories on the Origin of Pele’s Myth
The origins of Pele's myth remain a subject of ongoing debate and scholarly inquiry. Some theories suggest that the myth developed from observations of the volcanic activity in Hawaii, with the goddess embodying the power and unpredictability of natural forces. Others propose that Pele's mythology has connections to ancient Polynesian beliefs about fire and volcanic eruptions, suggesting a shared heritage among different island cultures.
One intriguing theory suggests that Pele’s myth is a manifestation of the island’s volcanic landscape and its connection to the Polynesian concept of ‘mana’ – a supernatural force that imbues certain objects and beings with extraordinary power. Pele’s association with volcanic activity and her fiery nature reflect the ‘mana’ attributed to the volcanoes and their power.
Regardless of its specific origins, the myth of Pele remains a powerful force in Hawaiian culture. It offers a framework for understanding the natural world, the power of the divine, and the complex relationship between humans and their environment.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. Is Pele a real god?
Pele is a mythical figure, a goddess in Hawaiian mythology. While she is not a real deity, her story reflects the Hawaiian people's understanding of the natural world and their reverence for the power of volcanoes.
2. What does Pele symbolize?
Pele embodies the power of fire, volcanoes, and creation in Hawaiian mythology. She symbolizes the cyclical nature of creation and destruction, the forces that shape the world, and the respect due to the natural order.
3. Where is Pele’s home?
Pele’s home is believed to be in the Hawaiian Islands, particularly the active volcanoes like Kilauea. Her fiery presence is felt throughout the archipelago, reminding the people of her power.
4. What are some of the most famous legends about Pele?
Some of the most famous legends about Pele include her rivalry with her sister Hiʻiaka, her jealousy over lovers, and her wrathful destruction of Kauaʻi. These stories illustrate Pele’s fiery nature, her intense passions, and her power over the natural world.
5. How do the Hawaiian people relate to Pele?
The Hawaiian people have a deep reverence for Pele. They offer rituals and gifts to appease her and seek her favor. They believe respecting her power brings blessings, while disrespecting her can incur her wrath.