The Baba Yaga in Eastern European Art: From Paintings to Sculptures
I. Introduction
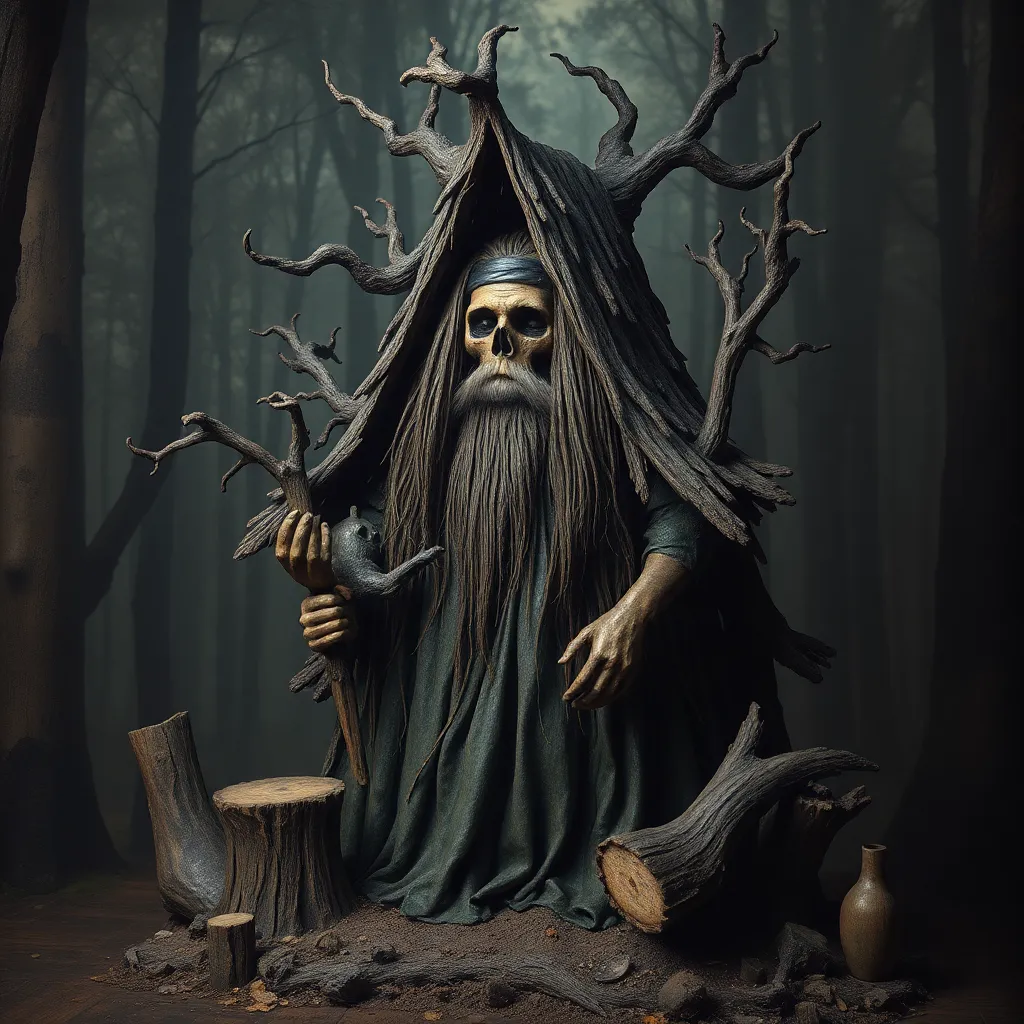
Baba Yaga is a prominent figure in Eastern European folklore, particularly within Slavic cultures. She is often depicted as a fearsome witch, residing deep in the forest in a hut that stands on chicken legs. This character embodies the complex nature of folklore, representing both the fears and the wisdom of the ancient world. The purpose of this article is to explore the various representations of Baba Yaga in different art forms, including paintings, sculptures, and modern interpretations. Over time, the image of Baba Yaga has evolved, reflecting changes in cultural attitudes and artistic styles.
II. The Origins of Baba Yaga in Folklore
Baba Yaga’s origins can be traced back to Slavic mythology, where she is often portrayed as both a villain and a guide. Historically, stories of Baba Yaga have been passed down through generations, evolving with each retelling. Her character is rich with symbolism and is often associated with the following:
- Nature and the wilderness: Baba Yaga is a guardian of the forest, representing the wild and untamed aspects of nature.
- Wisdom and knowledge: Despite her fearsome appearance, she is often sought out for her knowledge and magical abilities.
- Duality: Baba Yaga embodies the dual nature of life and death, serving as a bridge between the two realms.
This duality is what makes Baba Yaga such a compelling figure; she is both a source of fear and a provider of guidance. Her character challenges traditional notions of good and evil, inviting audiences to engage with her stories on a deeper level.
III. Baba Yaga in Traditional Paintings
Throughout the centuries, Baba Yaga has been a popular subject in Eastern European art, particularly in traditional paintings. Many artists have sought to capture her essence through various styles and interpretations.
A. Analysis of notable paintings featuring Baba Yaga
Some of the most notable artists who have depicted Baba Yaga include:
- Ivan Bilibin: Known for his illustrations of Russian folklore, Bilibin’s works often showcase Baba Yaga in a vibrant and whimsical light.
- Viktor Vasnetsov: His paintings frequently feature mythical characters, including Baba Yaga, portrayed in a more somber and mystical manner.
B. The role of color and technique in conveying Baba Yaga’s essence
Color and technique play a crucial role in the portrayal of Baba Yaga. Dark, earthy tones often symbolize her connection to the forest and the unknown, while bright colors can represent her magical powers. Techniques such as detailed line work and texture enhance the mystical quality of her character, making her both approachable and frightening.
IV. Baba Yaga in Modern Art
As cultural attitudes have shifted, so too has the representation of Baba Yaga in modern art. Contemporary artists have reinterpreted her character, often challenging traditional narratives.
A. Contemporary artists reinterpreting Baba Yaga
Modern artists such as Yelena Baturina and Elena Shumilova have created innovative works that explore Baba Yaga’s relevance in contemporary society. They may depict her in new contexts, blending traditional folklore with modern themes.
B. Evolution of style and medium in modern representations
The evolution of artistic styles has also influenced how Baba Yaga is portrayed. From abstract interpretations to mixed-media works, artists are experimenting with various mediums to express her complexity.
C. The impact of cultural shifts on Baba Yaga’s portrayal
As feminist movements and discussions about gender roles have emerged, Baba Yaga’s character has been reexamined. She is often viewed through a lens that emphasizes her independence and strength, transforming her from a mere villain to a symbol of empowerment.
V. Sculptural Representations of Baba Yaga
Sculpture offers a three-dimensional perspective on Baba Yaga, allowing viewers to engage with her character in a more tactile way.
A. Overview of significant sculptures depicting Baba Yaga
Several notable sculptures have been created to represent Baba Yaga, ranging from large public installations to intimate pieces in galleries. Artists often depict her in dynamic poses, accentuating her dual nature.
B. Materials and techniques used in sculpting her image
Artists utilize a variety of materials, including:
- Wood: Symbolic of her connection to nature, many sculptures feature carved wood to evoke the essence of the forest.
- Bronze: This material allows for intricate details and durability, often used in larger outdoor installations.
C. Analysis of how three-dimensional art alters the perception of her character
The three-dimensional nature of sculpture allows for a more immersive experience. Viewers can walk around the piece, gaining different perspectives and interpretations, which adds depth to their understanding of Baba Yaga’s multifaceted character.
VI. Baba Yaga in Performance Art and Installations
Performance art and installations provide a unique platform for exploring Baba Yaga’s story in a dynamic way.
A. Exploration of performance art featuring Baba Yaga
Modern performance artists have incorporated Baba Yaga into their works, using her narrative to address contemporary issues such as feminism, identity, and cultural heritage.
B. Installations that incorporate her folklore into immersive experiences
Installations often create immersive environments where audiences can engage with Baba Yaga’s world. These experiences can include interactive elements, allowing participants to explore folklore in a personal way.
C. The role of audience interaction in modern interpretations
Audience interaction transforms the experience of Baba Yaga from a passive observation to an active participation, encouraging viewers to reflect on their own connections to the folklore.
VII. Comparative Analysis of Baba Yaga in Different Art Forms
Examining Baba Yaga across various art forms reveals significant contrasts and insights into her character.
A. Contrasts between two-dimensional and three-dimensional representations
While traditional paintings can encapsulate a moment in time, sculptures allow for a more comprehensive exploration of her character. This difference impacts how audiences perceive her complexities.
B. The significance of narrative in paintings vs. sculptures
Paintings often tell a story through symbolism and chosen imagery, while sculptures may invite viewers to interpret the narrative based on their physical interaction with the piece.
C. How various mediums influence the audience’s understanding of Baba Yaga
Different mediums evoke distinct emotional responses, shaping how audiences connect with Baba Yaga’s character and the themes of her stories.
VIII. Conclusion
Baba Yaga’s representation in Eastern European art has evolved significantly from traditional folklore to modern interpretations. As a character that embodies both fear and wisdom, she continues to resonate with contemporary audiences. The enduring legacy of Baba Yaga illustrates the importance of preserving folklore through art, ensuring that her stories and symbolism remain relevant in today’s cultural landscape. Ultimately, Baba Yaga serves as a powerful reminder of the complexities of human nature, inviting us to explore the depths of our own narratives through the lens of art.