The Dragon’s Breath: Exploring the Elements of Fafnir’s Power
I. Introduction to Fafnir
Fafnir is one of the most notable figures in Norse mythology, often depicted as a fearsome dragon. Originally a dwarf, Fafnir’s transformation into a dragon is steeped in themes of greed and betrayal, making him a complex character within the mythological canon. Dragons in mythology are not merely monstrous creatures; they represent various elements such as chaos, greed, and the struggle for power. This article aims to explore the elements of Fafnir’s power, focusing on his origins, symbolism, and the lessons his story imparts.
II. The Mythological Origins of Fafnir
Fafnir’s origins trace back to the Volsunga saga, where he is initially portrayed as a dwarf. His transformation from a dwarf to a dragon is a pivotal moment in his narrative, driven by insatiable greed. The story revolves around a cursed hoard of gold, known as the Rheingold, which brings about Fafnir’s demise and transformation.
- Fafnir’s Transformation: Consumed by greed, Fafnir murders his father, Hreidmar, to obtain the treasure and subsequently becomes a dragon, embodying the very greed that corrupted him.
- The Curse of the Gold: The gold is cursed by the Nibelung, leading to tragic consequences for anyone who possesses it.
This myth serves as a warning about the destructive power of greed and its ability to warp one’s nature, turning them into something monstrous.
III. The Symbolism of Fire in Fafnir’s Breath
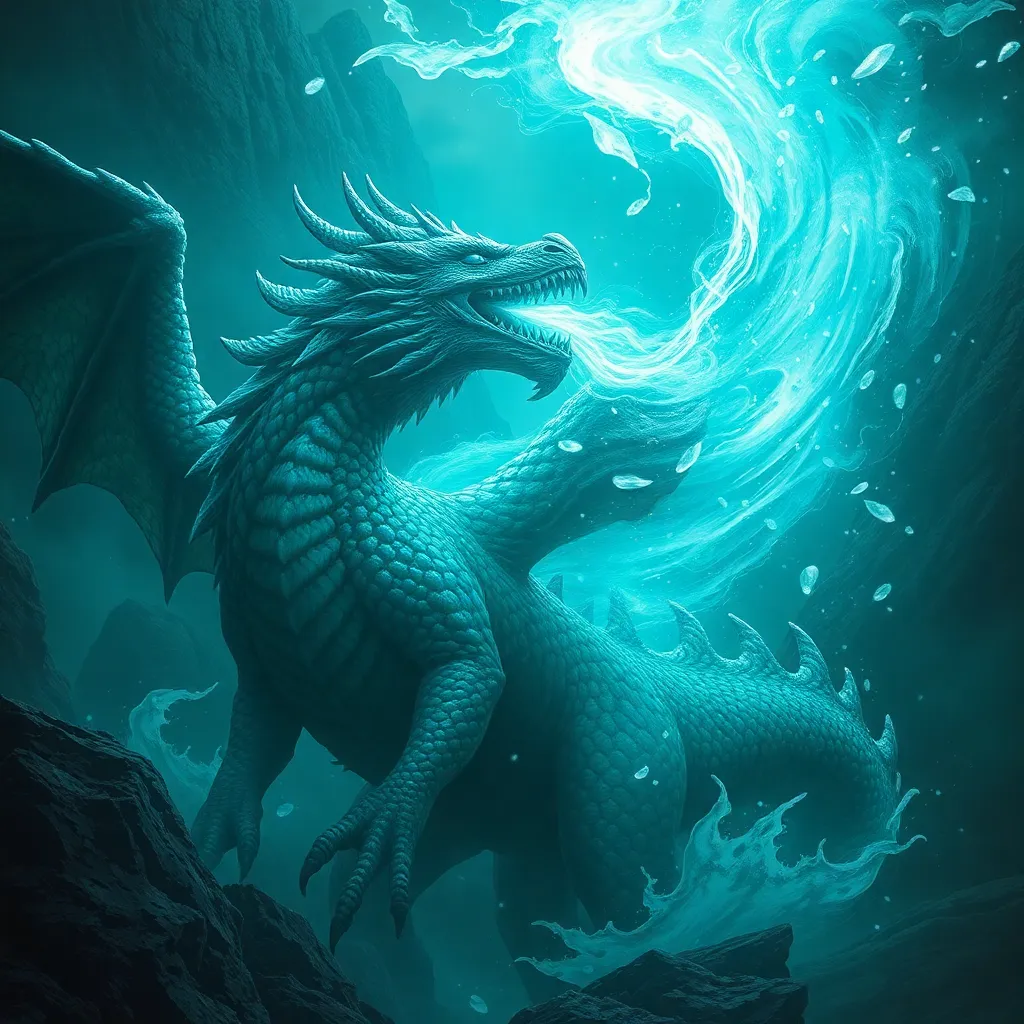
Fafnir’s breath is often referred to as “dragon’s breath,” a potent weapon that symbolizes destruction. Fire in mythology frequently represents duality: it can both destroy and purify, symbolizing the cycle of death and rebirth.
- Dragon’s Breath as a Weapon: Fafnir’s fiery breath is not just a method of attack; it symbolizes his overwhelming power and ferocity.
- Fire as Destruction and Rebirth: The fire can annihilate entire landscapes, yet it also holds the potential for regeneration, paralleling themes in nature.
When compared to other mythological creatures, such as Smaug from J.R.R. Tolkien’s “The Hobbit,” Fafnir’s fire serves a similar purpose, representing the ultimate weapon of a creature that has become a victim of its own greed.
IV. The Role of Wealth and Greed
The cursed gold in Fafnir’s story is central to understanding his character and motivations. Wealth in many mythological narratives often serves as a double-edged sword, leading to both power and downfall.
- Significance of Cursed Gold: The gold represents unattainable wealth that ultimately brings tragedy.
- Greed’s Role: Fafnir’s greed transforms him from a dwarf into a dragon, illustrating how the desire for wealth can lead to one’s undoing.
The broader moral lessons surrounding wealth in mythology highlight the perils of greed, reminding us that the pursuit of material wealth can consume and destroy individuals and relationships.
V. The Connection Between Fafnir and Nature
Fafnir’s power is intrinsically linked to elemental forces, particularly earth and fire. As a dragon, he embodies a fierce guardian of treasure and natural resources, showcasing the interplay between nature and mythological creatures.
- Elemental Representation: Fafnir’s dragon form symbolizes the untamed aspects of nature, representing both beauty and terror.
- Guardian of Treasure: His role as a dragon also signifies the protection of natural resources, highlighting the importance of balance within nature.
The connection between Fafnir and nature emphasizes how mythology often reflects the human experience with the environment and the respect owed to its power.
VI. The Hero’s Journey: The Quest to Defeat Fafnir
The tale of Fafnir culminates in the heroic narrative of Siegfried, who embarks on a quest to slay the dragon. This encounter is not merely a battle between hero and monster; it represents the triumph of courage over fear.
- Siegfried’s Encounter: Armed with bravery and cunning, Siegfried confronts Fafnir, showcasing the hero’s journey archetype.
- Significance of Bravery: The battle emphasizes the virtues of courage, intelligence, and the ability to face overwhelming odds.
Siegfried’s victory over Fafnir is not just a personal triumph; it is a metaphor for overcoming one’s inner demons and the challenges that life presents.
VII. Fafnir’s Legacy in Modern Culture
Fafnir’s legacy extends beyond ancient texts, influencing literature, art, and contemporary storytelling. His character has evolved, reflecting modern themes while retaining core elements of his mythological origins.
- Representation in Literature and Art: Fafnir appears in various adaptations, often symbolizing greed and the consequences of ambition.
- Influence on Fantasy Genres: His archetype has inspired countless dragon characters in fantasy literature and games, shaping the genre’s conventions.
This evolution illustrates how mythological figures can adapt to contemporary narratives, retaining relevance in modern storytelling.
VIII. Conclusion
Fafnir’s enduring power and symbolism serve as a testament to the complexities of human nature, particularly our relationship with greed and ambition. His story offers profound moral lessons, reminding us of the dangers of allowing desires to dictate our actions. As we reflect on Fafnir’s legacy, it becomes clear that mythological elements continue to resonate, providing insights into contemporary issues and the human condition.