The Dragon’s Shadow: Fafnir’s Influence on the Development of Norse Mythology
I. Introduction
Norse mythology is rich with complex characters and narratives, among which the dragon Fafnir stands out as a significant figure. Fafnir, originally a dwarf, embodies the darker aspects of ambition, greed, and transformation. This article aims to explore Fafnir’s influence on the development of Norse mythology, particularly focusing on how his story interweaves with the themes of heroism, wealth, and the archetype of dragons within mythological narratives.
II. Fafnir’s Origins and Transformation
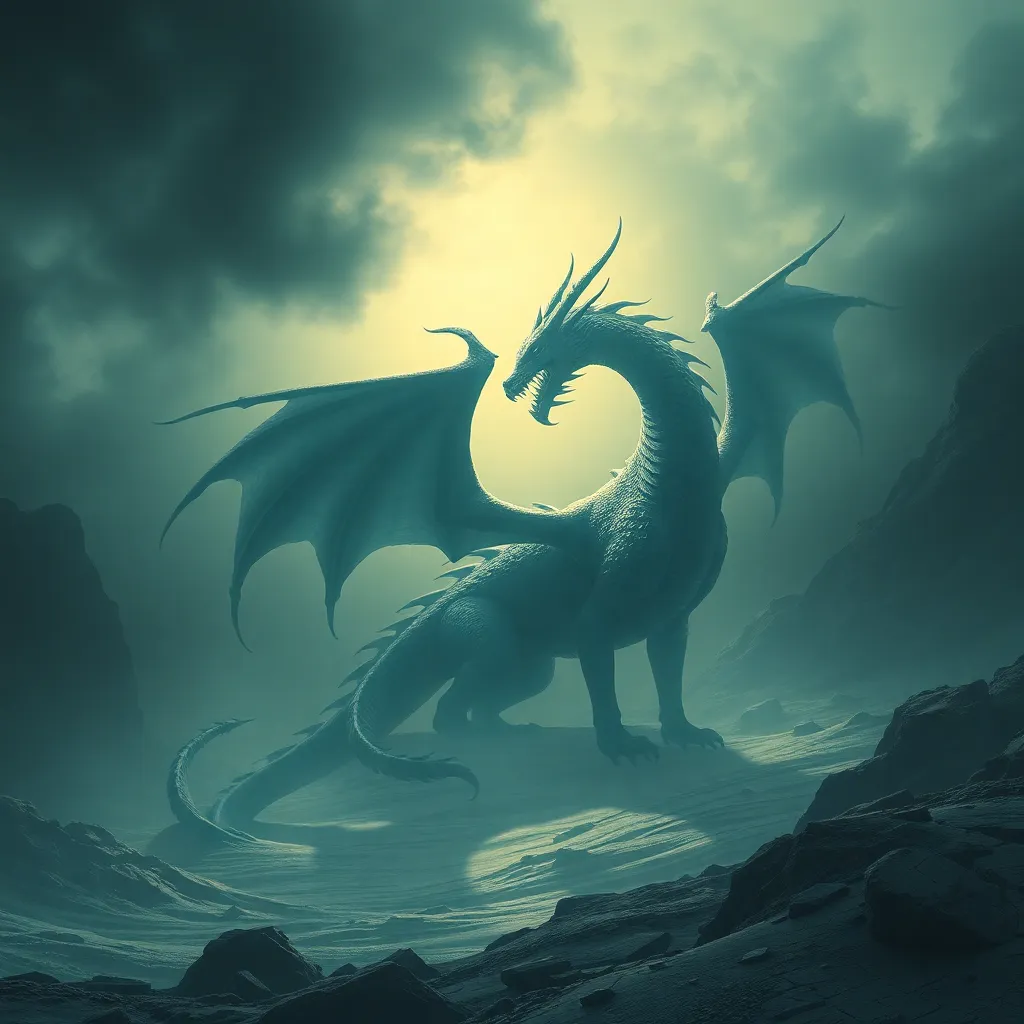
The story of Fafnir is primarily chronicled in the Volsunga Saga, where he begins as a dwarf who is enchanted by the allure of gold. The tale details his transformation from a dwarf into a fearsome dragon, a metamorphosis fueled by insatiable greed. This transformation serves as a powerful metaphor for how ambition and desire can corrupt an individual, leading to their downfall.
- Initial Transformation: Fafnir, driven by greed, murders his father to seize the cursed gold.
- Dragon Form: His transformation into a dragon symbolizes the complete loss of his humanity and the overwhelming nature of greed.
The symbolism of greed is central to Fafnir’s character development, illustrating the destructive power of avarice in Norse culture. His journey from a dwarf to a dragon serves as a cautionary tale about the consequences of unbridled ambition.
III. The Role of Fafnir in the Heroic Narrative
Fafnir’s role as a formidable antagonist in Norse heroic tales is crucial, particularly in his connection to the hero Sigurd. Sigurd’s quest to slay Fafnir is driven by a desire for glory and the treasures that the dragon guards. This confrontation embodies several key themes:
- Bravery: Sigurd must summon immense courage to face the monstrous dragon.
- Fate and Destiny: The heroic narrative often intertwines with the themes of fate, suggesting that Sigurd’s battle with Fafnir is preordained.
The conflict between Sigurd and Fafnir is not merely a physical battle; it represents the struggle between good and evil, ambition and consequence, and the hero’s journey to self-discovery.
IV. The Symbolism of Dragons in Norse Mythology
Dragons in Norse mythology are often depicted as embodiments of chaos and destruction. Fafnir stands out among these creatures, representing the catastrophic potential of greed and the dark side of ambition. In contrast to other dragon figures in Norse lore, Fafnir’s transformation highlights a deeper moral lesson about the dangers of coveting wealth.
- Chaos and Destruction: Dragons are frequently portrayed as destructive forces that heroes must overcome.
- Comparative Analysis: Other dragons, such as Nidhogg, also symbolize destruction but with different narratives and implications.
Through these representations, Fafnir’s character reinforces the notion that dragons are not only physical threats but also symbolic of deeper human flaws.
V. Fafnir’s Influence on Later Mythological Texts
The legacy of Fafnir extends beyond Norse mythology, influencing medieval literature and even contemporary storytelling. His themes resonate across cultures, where similar motifs of dragons guarding treasures and the consequences of greed appear in various mythologies.
- Medieval Literature: Fafnir’s story inspired countless tales of knights and dragons, shaping the narrative traditions of Europe.
- Cultural Analysis: Many cultures have legends of dragons that mirror Fafnir’s themes, highlighting the universal nature of these narratives.
- Modern Influence: Fafnir has influenced modern fantasy literature and media, appearing in books, films, and games that explore similar archetypes.
This cross-cultural influence underscores Fafnir’s significance as a mythological figure whose themes remain relevant in contemporary narratives.
VI. Fafnir and the Concept of Wealth
The curse of the gold that Fafnir hoards serves as a critical aspect of his story. In Norse culture, wealth is depicted as a double-edged sword, bringing both fortune and ruin.
- The Curse: The gold is cursed, leading to Fafnir’s downfall and transforming him into a monster.
- Cautionary Tale: Fafnir’s story warns against the dangers of greed and the moral decay it can cause.
Fafnir’s tale serves as a timeless reminder that the pursuit of wealth can lead to dire consequences, making it a significant element of the moral landscape in Norse mythology.
VII. The Archetype of the Dragon in Modern Narratives
The archetype of the dragon has evolved significantly since the days of Norse mythology. Fafnir’s legacy can be seen in contemporary interpretations of dragons, which often explore themes of power, greed, and the battle between good and evil.
- Evolution of the Archetype: Dragons have transitioned from embodiments of chaos to complex characters with their own narratives.
- Contemporary Influence: Modern storytelling, including films and video games, draws heavily on Fafnir’s archetype, reflecting his impact on popular culture.
This evolution highlights the adaptability of mythological figures and their capacity to resonate with new generations.
VIII. Conclusion
Fafnir’s significance in Norse mythology cannot be overstated. As a representation of greed, chaos, and the hero’s journey, his story continues to influence modern narratives and cultural expressions. The enduring legacy of Fafnir and dragon figures serves as a testament to the power of myth in shaping our understanding of human nature and moral lessons. In contemporary culture, these ancient tales remind us of the timelessness of their themes and the relevance of their messages in our lives today.