The Griffin’s Legacy in Persian Art and Architecture
I. Introduction
The Griffin, a legendary creature with the body of a lion and the head and wings of an eagle, has captivated the imaginations of many civilizations throughout history. In Persian culture, the Griffin is not merely a mythical beast; it represents strength, protection, and divine power. Its significance in Persian mythology and art is profound, influencing various aspects of cultural expression from ancient times to the present.
This article aims to explore the Griffin’s influence in Persian art and architecture, delving into its historical roots, artistic representations, architectural significance, and its enduring legacy in contemporary society.
II. Historical Context of the Griffin in Persian Mythology
The origins of the Griffin can be traced back to ancient civilizations, including the Mesopotamians and Egyptians, where it was often associated with the divine and the supernatural. In Persian mythology, the Griffin evolved as a symbol that embodied both the ferocity of a lion and the majesty of an eagle, making it a creature of great importance.
Over the centuries, the Griffin’s representation in Persian culture has transformed, reflecting changes in artistic styles and societal values. Initially depicted in a more abstract form, the Griffin gradually became a more detailed and lifelike representation in the art of subsequent eras.
III. The Griffin in Persian Art
The Griffin has been prominently featured in various ancient Persian artifacts, such as pottery, metalwork, and textiles. These depictions often illustrate the creature in dynamic poses, emphasizing its power and grace.
- Ancient Persian Artifacts: Items such as the Achaemenid seals often showcase the Griffin in intricate designs, symbolizing royalty and divine protection.
- Artistic Styles: The portrayal of the Griffin has varied with different artistic movements, from the detailed engravings of the Achaemenid period to the more stylized forms seen in later Islamic art.
- Iconography: In Persian art, the Griffin is often associated with themes of guardianship and strength, frequently appearing alongside other mythological creatures.
IV. Architectural Significance of the Griffin
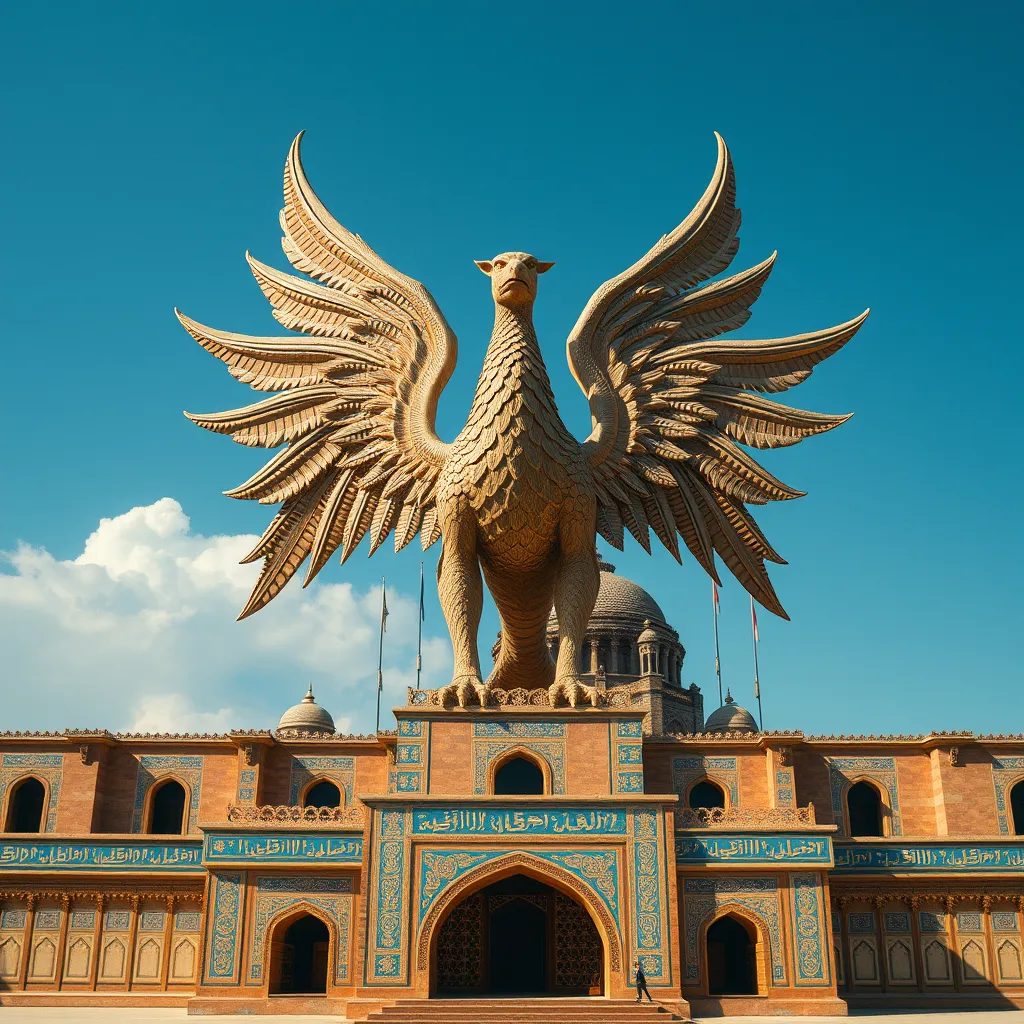
In addition to its presence in art, the Griffin holds a significant place in Persian architecture. It has been used as a decorative motif in various structures, imparting a sense of grandeur and protection.
- Decorative Motif: The Griffin appears in the ornamentation of palaces, mosques, and public buildings, symbolizing divine protection over the space.
- Notable Structures: The Apadana Palace at Persepolis and various mosques throughout Iran feature Griffin imagery, showcasing its architectural significance.
- Symbolism: In architecture, the Griffin serves as a guardian figure, meant to protect the inhabitants and visitors of the structure.
V. Regional Variations of Griffin Representations
The representation of the Griffin in Persian culture is not monolithic; it varies significantly across different regions of Persia. These regional differences highlight the diverse cultural influences that shaped Persian artistry.
- Regional Differences: In regions like Fars and Khorasan, the Griffin may be depicted with varying degrees of stylization and detail, influenced by local artistic traditions.
- Cultural Exchanges: The interaction with neighboring cultures, such as the Greeks and Indians, has led to the incorporation of new elements into Griffin representations.
- Comparative Analysis: When compared to other cultures, such as the Greek and Egyptian interpretations, the Persian Griffin reflects a unique blend of local and external influences.
VI. The Griffin’s Legacy in Contemporary Persian Art and Architecture
In modern times, the Griffin has experienced a revival in Persian art, symbolizing national identity and cultural heritage. Contemporary artists and architects are drawing inspiration from this ancient symbol to create works that resonate with both tradition and modernity.
- Revival in Art: Many modern Persian artists incorporate Griffin motifs into their works, celebrating the creature’s historical significance while reinterpreting it for contemporary audiences.
- Contemporary Architecture: Architects in Iran are revisiting traditional designs that feature Griffin imagery, merging old symbols with new architectural innovations.
- National Identity: The Griffin has become a symbol of national pride, representing the rich cultural heritage of Persia and its historical significance.
VII. Challenges and Preservation Efforts
Despite its rich history, the preservation of Griffin-related art and architecture faces several challenges. Modernization, urbanization, and neglect threaten the survival of these cultural artifacts.
- Threats to Preservation: Many ancient sites and artifacts are at risk due to environmental factors and lack of funding for conservation efforts.
- Preservation Initiatives: Various institutions and artists are working to maintain and restore Griffin-related art, raising awareness about its importance.
- Education and Awareness: Promoting education about Persian cultural heritage is crucial for fostering appreciation and support for preservation efforts.
VIII. Conclusion
The Griffin’s impact on Persian art and architecture is profound and enduring. This mythological symbol has transcended time, reflecting the values and beliefs of Persian culture while continuing to inspire contemporary expressions of identity and heritage.
As we reflect on the legacy of the Griffin, it is essential to recognize the importance of preserving such cultural symbols. Continued research and preservation initiatives are vital to ensure that future generations can appreciate and learn from the rich tapestry of Persian history and mythology.