The Peryton’s Wings: Exploring the Egyptian Mythological Concept of Flight
I. Introduction to the Peryton
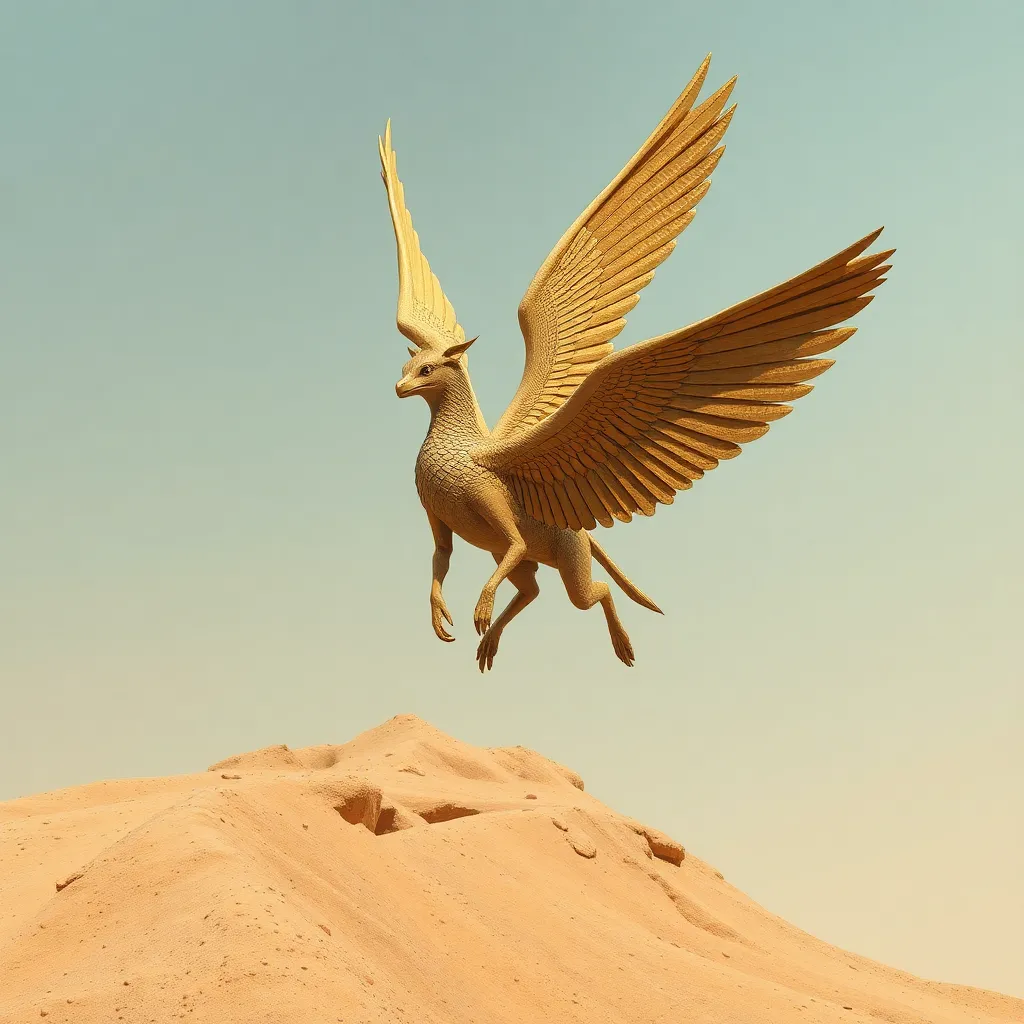
The Peryton is a captivating creature rooted in the rich tapestry of Egyptian mythology. Often depicted as a hybrid being with the body of a deer and the wings of a bird, the Peryton embodies the duality of earth and sky. Its origins can be traced back to ancient texts and art, where it symbolizes various aspects of life, death, and the journey of the soul.
In Egyptian culture, flight carries profound significance. It represents not only the freedom of the spirit but also the connection between the earthly realm and the divine. The Peryton, with its majestic wings, serves as a powerful symbol of this connection, illustrating the importance of ascension and transcendence in the beliefs of ancient Egyptians.
II. The Symbolism of Wings in Ancient Egypt
Wings in Egyptian mythology are often associated with several key themes:
- Divine Protection: Wings are seen as a protective force, often depicted in the form of deities who shield and guide souls.
- Freedom: The act of flight symbolizes liberation from earthly ties and the ability to traverse between realms.
- Transformation: Wings signify the potential for transformation and rebirth, a crucial concept in the Egyptian belief system.
In this context, the Peryton emerges as a significant figure, embodying the essence of wings as both protective and liberating forces within mythology.
III. The Peryton in Egyptian Lore
The Peryton is characterized by its unique appearance and attributes. It is often described as having the graceful body of a stag combined with expansive, feathered wings, allowing it to soar through the skies. This duality reflects its role as a mediator between the earthly realm and the heavens.
In Egyptian folklore, the Peryton serves various roles. It is sometimes seen as a guardian spirit, guiding the souls of the deceased on their journey to the afterlife. Its wings symbolize the passage from life to death and the hope of rebirth, making it an integral part of myths surrounding the afterlife.
IV. Comparative Mythology: The Peryton and Other Winged Creatures
When examining the Peryton, it becomes evident that it shares similarities with other winged beings found in Egyptian mythology:
- Horus: The falcon-headed god represents kingship and the sky, embodying the protective and guiding aspects of flight.
- Isis: Often depicted with outstretched wings, she symbolizes protection and motherhood, emphasizing the nurturing aspect of flight.
Furthermore, the concept of winged creatures is not unique to Egyptian mythology. Many cultures feature similar beings, such as:
- Greek Mythology: The griffin, a creature with the body of a lion and the head and wings of an eagle, symbolizes strength and vigilance.
- Mesopotamian Mythology: The Lamassu, a protective deity with a human head and the body of a lion or bull, features wings that signify its divine nature.
These comparative elements highlight the universal symbolism of wings across different cultures, emphasizing the connection between humanity and the divine.
V. The Peryton’s Connection to the Afterlife
In Egyptian thought, flight is a powerful metaphor for the soul’s journey after death. The Peryton plays a significant role in this narrative:
- Flight as Ascension: The act of flying symbolizes the soul’s ascension to the afterlife, representing liberation from the physical body.
- Guidance: The Peryton is often seen as a guide for souls, leading them safely through the trials of the afterlife.
- Transformation: Its ability to navigate between realms reinforces the idea of transformation inherent in the death and rebirth cycle.
In Egyptian funerary practices, the Peryton is invoked as a protective presence, ensuring a safe passage for the deceased into the afterlife.
VI. Artistic Representations of the Peryton
The Peryton has been depicted in various forms of ancient Egyptian art. Iconography often portrays it in vibrant colors, emphasizing its wings and ethereal nature. Common representations include:
- Wall Paintings: Depictions in tombs and temples, showcasing the Peryton alongside gods and other mythological figures.
- Amulets: Small charms featuring the Peryton, believed to offer protection and guidance to the wearer.
In modern times, the Peryton has been reinterpreted in various ways, appearing in literature and visual arts, often symbolizing freedom, protection, and the mysteries of life and death.
VII. The Legacy of the Peryton in Contemporary Culture
The influence of Egyptian mythology, including the Peryton, can be seen in contemporary literature and media:
- Fantasy Literature: The Peryton’s characteristics have inspired numerous fantasy authors, leading to the creation of winged creatures in modern narratives.
- Popular Media: Films and video games often reference Egyptian mythology, incorporating elements like the Peryton to enrich their storytelling.
This enduring fascination with the Peryton and similar mythological creatures underscores the timeless appeal of flight and the significance of wings in our understanding of the world.
VIII. Conclusion
In conclusion, the Peryton holds a unique place in Egyptian mythology, symbolizing the profound relationship between flight, protection, and the journey of the soul. Its significance extends beyond ancient texts and art, influencing contemporary culture and literature.
As we reflect on the Peryton and its enduring legacy, we recognize the universal allure of flight in mythological contexts, reminding us of our aspirations, hopes, and the eternal quest for freedom and transcendence.