The Role of Amun in Egyptian Mythology
In Egyptian mythology, Amun was one of the most prominent and powerful deities, often referred to as the ‘King of the Gods.’ Let’s explore the significant role this divine figure played in the ancient Egyptian belief system.
1. Who was Amun in Egyptian mythology?
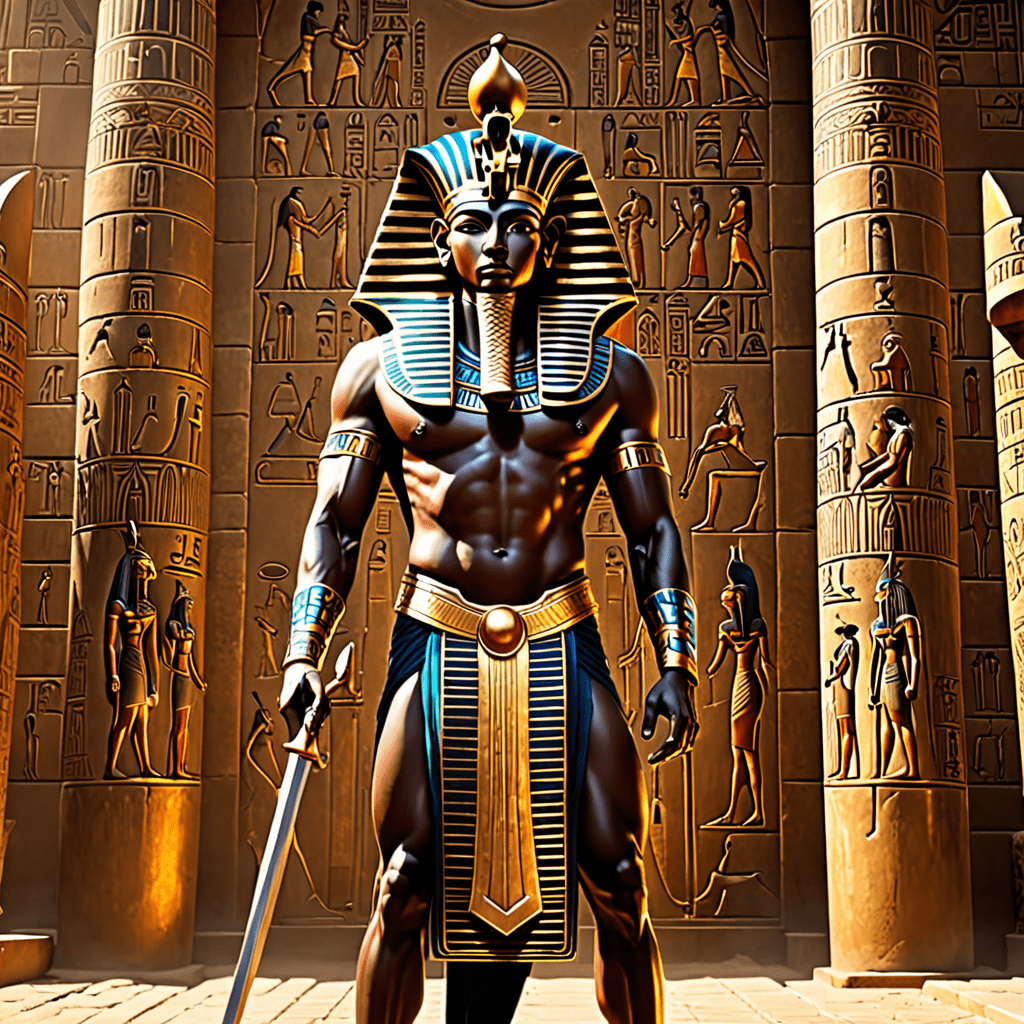
Amun, whose name means “hidden” or “invisible,” was initially a local deity in Thebes. Over time, he rose to national prominence and became associated with the sun god, Ra, forming the powerful combination known as Amun-Ra. This union symbolized the sunrise, representing creation and renewal.
2. What were Amun’s attributes and associations?
Amun was often depicted as a man wearing a double-plumed crown or as a ram-headed figure. He was recognized as the god of air and the breath of life, linked to fertility and the sustenance of living beings. Amun was also regarded as a protector of the poor and those in need, showcasing his compassion and benevolence.
3. What role did Amun play in Egyptian society?
As the supreme god of the Egyptians during the New Kingdom, Amun held considerable sway over the spiritual and political realms. Pharaohs frequently identified themselves with Amun, strengthening their authority and claiming divine endorsement for their rule. The wealth and influence of the priesthood of Amun at Thebes reached unparalleled levels, highlighting his significance in society.
4. What was the significance of the Cult of Amun?
The Cult of Amun, centered in Karnak, was incredibly influential. It controlled vast temple complexes, land, and resources, making Amun one of the wealthiest gods in the Egyptian pantheon. The priests of Amun enjoyed considerable power and played crucial roles in rituals, ceremonies, and the governance of the country, showcasing the pervasive impact of Amun’s cult on Egyptian life.
FAQ about the Role of Amun in Egyptian Mythology
Who is Amun in Egyptian Mythology?
Amun, also known as Amun-Ra, was a prominent deity in ancient Egyptian mythology. He was considered the king of the gods, associated with the sun and air. Amun was often depicted as a man wearing a double-plumed crown, holding a whip and an ankh, symbolizing power and life.
What was Amun’s Role in Egyptian Mythology?
Amun played a crucial role as a creator god and the patron deity of Thebes. He was believed to rule over the skies, granting pharaohs divine authority and protecting the people. Amun was also associated with fertility, ensuring the land’s prosperity and abundance.
Why was Amun Important in Ancient Egypt?
Amun’s significance extended beyond religion; he was central to the concept of kingship and the divine right of pharaohs. His fusion with the sun god Ra elevated his status, symbolizing the sun’s daily journey across the sky and its life-giving properties.
How was Amun Worshipped in Ancient Egypt?
Amun was revered through elaborate rituals and grand temples dedicated to his worship, such as the Karnak Temple in Thebes. Priests played a vital role in caring for Amun’s cult image and performing ceremonies to honor him