The Roots of Fear: Níðhöggr and the Human Psyche
I. Introduction
Fear is a universal emotion that transcends cultures and epochs, manifesting in various forms that can both protect and paralyze. It is an instinctual response, deeply embedded in human nature, serving as a survival mechanism that alerts us to potential dangers. In Norse mythology, one of the most compelling symbols of fear is Níðhöggr, a dragon that embodies the darker aspects of existence and the subconscious fears that plague humanity.
This article aims to explore the connection between Níðhöggr and the human psyche, delving into how this mythical figure can provide insights into our understanding of fear and its implications for our lives.
II. Understanding Níðhöggr: The Dragon of Norse Mythology
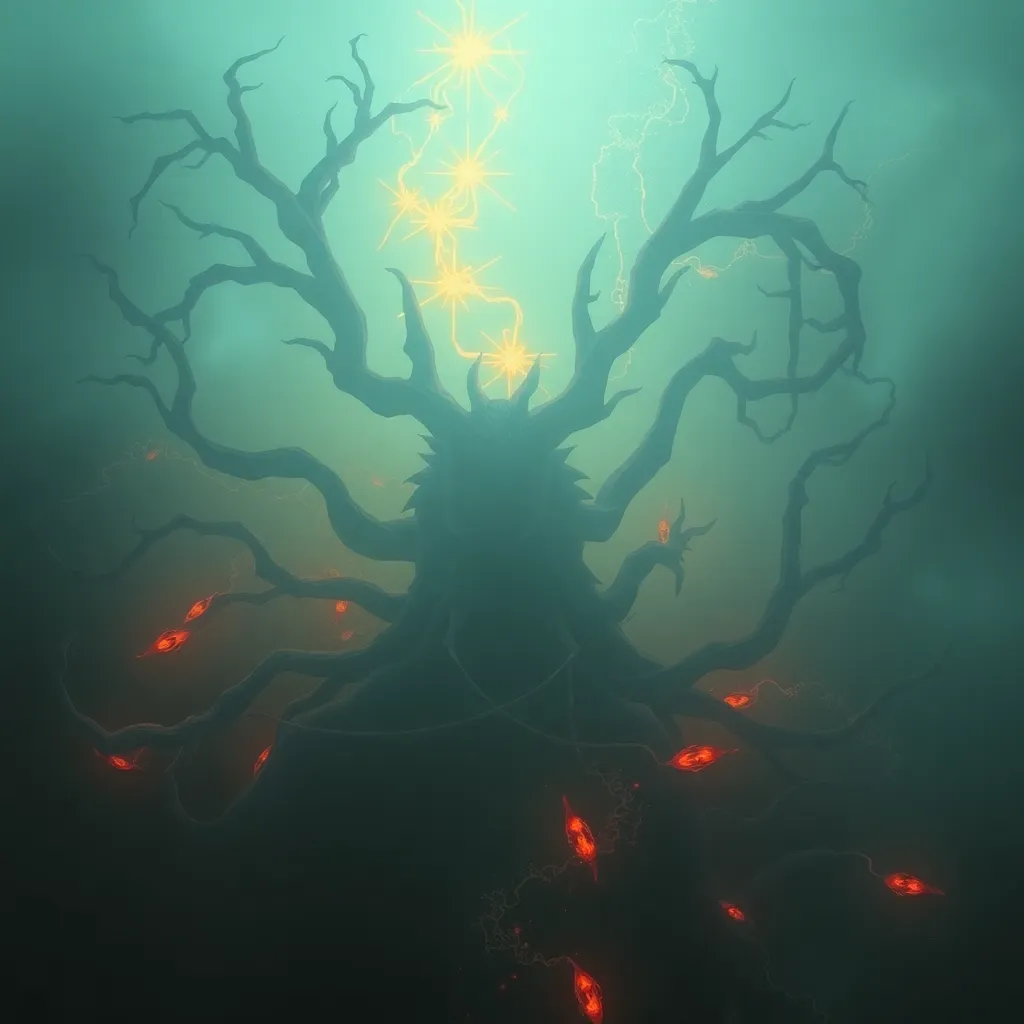
Níðhöggr is depicted as a serpent or dragon that gnaws at the roots of Yggdrasil, the World Tree, in Norse cosmology. This creature is not merely a monster but a symbol of the fears and anxieties that dwell within the human psyche.
A. Description and attributes of Níðhöggr
Níðhöggr is often described as a fearsome creature with a grotesque form, embodying decay and destruction. Its presence is a constant reminder of the inevitability of death and the chaos that lurks beneath the surface of existence.
B. Role of Níðhöggr in the mythological narrative
In the mythological narrative, Níðhöggr plays a critical role in the cycle of life and death. By gnawing at the roots of Yggdrasil, it symbolizes the destructive forces that threaten the stability of the cosmos, representing the fears that can undermine our lives.
C. Symbolism associated with Níðhöggr in the context of fear
The symbolism of Níðhöggr extends beyond its physical form. It represents:
- The fear of death and the unknown
- The anxiety of losing control over one’s life
- The consequences of unchecked emotions and desires
III. The Nature of Fear: Psychological Perspectives
Fear is a complex emotion with deep psychological roots. Understanding its nature can illuminate the ways it affects our behavior and choices.
A. Definition of fear and its evolutionary significance
Fear can be defined as an emotional response to perceived threats or danger. From an evolutionary perspective, it has played a crucial role in survival, prompting individuals to react swiftly to threats, thus ensuring their safety.
B. Different types of fear: rational vs. irrational
Fear can be categorized into two primary types:
- Rational fear: This type of fear is based on real threats and is often adaptive. For example, fear of heights can prevent dangerous falls.
- Irrational fear: Also known as phobias, these fears are disproportionate to the actual threat, such as fear of spiders or flying.
C. The physiological and psychological responses to fear
When faced with fear, the body undergoes a physiological response known as the “fight or flight” reaction, which includes:
- Increased heart rate
- Rapid breathing
- Heightened alertness
Psychologically, fear can lead to avoidance behaviors, anxiety, and in extreme cases, panic attacks.
IV. Fear and the Human Psyche: A Deep Dive
Fear is more than just a response; it shapes our behaviors and decisions in profound ways.
A. How fear shapes behavior and decision-making
Fear influences our choices, often leading to risk-averse behavior. It can prevent us from pursuing opportunities or engaging in activities that could lead to personal growth.
B. The impact of fear on mental health
Chronic fear can have detrimental effects on mental health, contributing to conditions such as anxiety disorders, depression, and post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD).
C. Fear as a catalyst for growth and resilience
Despite its negative aspects, fear can also serve as a catalyst for personal growth. Confronting fears can lead to:
- Increased resilience
- Greater self-awareness
- Empowerment through overcoming challenges
V. Mythology and the Human Experience: Lessons from Níðhöggr
Níðhöggr’s narrative offers valuable lessons about the nature of fear and how it shapes the human experience.
A. Analyzing the allegorical significance of Níðhöggr’s character
Níðhöggr can be seen as an allegory for the fears that lurk in our subconscious, representing the chaos that threatens to consume us if left unchecked.
B. How myths reflect collective fears of society
Myths often encapsulate the collective fears of a society, providing a framework for understanding complex emotions and experiences. Níðhöggr, as a figure of fear, reflects the anxieties of the Norse people regarding death, destruction, and the unknown.
C. The role of storytelling in confronting and understanding fear
Storytelling serves as a powerful tool for addressing fear. By engaging with narratives like that of Níðhöggr, individuals can confront their fears in a safe context, facilitating understanding and acceptance.
VI. Cultural Interpretations of Fear: Beyond Norse Mythology
Exploring fear in different cultural contexts reveals its universality and the various ways societies have grappled with it.
A. Comparison of Níðhöggr with fear symbols in other cultures
Many cultures have symbols that represent fear:
- Dragons in Chinese mythology: Often seen as protectors, they also embody chaos and the unknown.
- The Minotaur in Greek mythology: Represents the fear of the beast within and the darkness of human nature.
B. The universality of fear across different mythologies
Fear is a common theme across mythologies, reflecting the shared human experience of facing the unknown and confronting mortality.
C. Lessons learned from various cultural approaches to fear
Different cultures provide unique insights into managing fear, often emphasizing communal support, rituals, and the importance of storytelling in processing and overcoming fear.
VII. Navigating Fear: Strategies for the Modern Individual
In today’s fast-paced world, understanding and managing fear is crucial for mental well-being.
A. Techniques for confronting and managing fear
Several techniques can be effective in confronting fear, including:
- Mindfulness and meditation
- Cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT)
- Gradual exposure to feared situations
B. The role of therapy and self-help in overcoming fear
Professional therapy can provide tools and strategies to deal with fear, while self-help resources encourage individuals to actively engage with their fears.
C. Embracing fear as a part of personal growth
By reframing fear as a natural part of life, individuals can learn to embrace it, using it as a stepping stone toward personal growth and resilience.
VIII. Conclusion
Níðhöggr serves as a profound symbol of fear in Norse mythology, offering valuable insights into the nature of fear itself. By exploring the connections between this mythical dragon and the human psyche, we can better understand our own fears and the ways they shape our lives.
In integrating mythological insights with psychological understanding, we can encourage ourselves and others to explore personal fears and their roots, fostering a journey toward acceptance and resilience.