The Thunderbird: A Symbol of Nature’s Power
I. Introduction
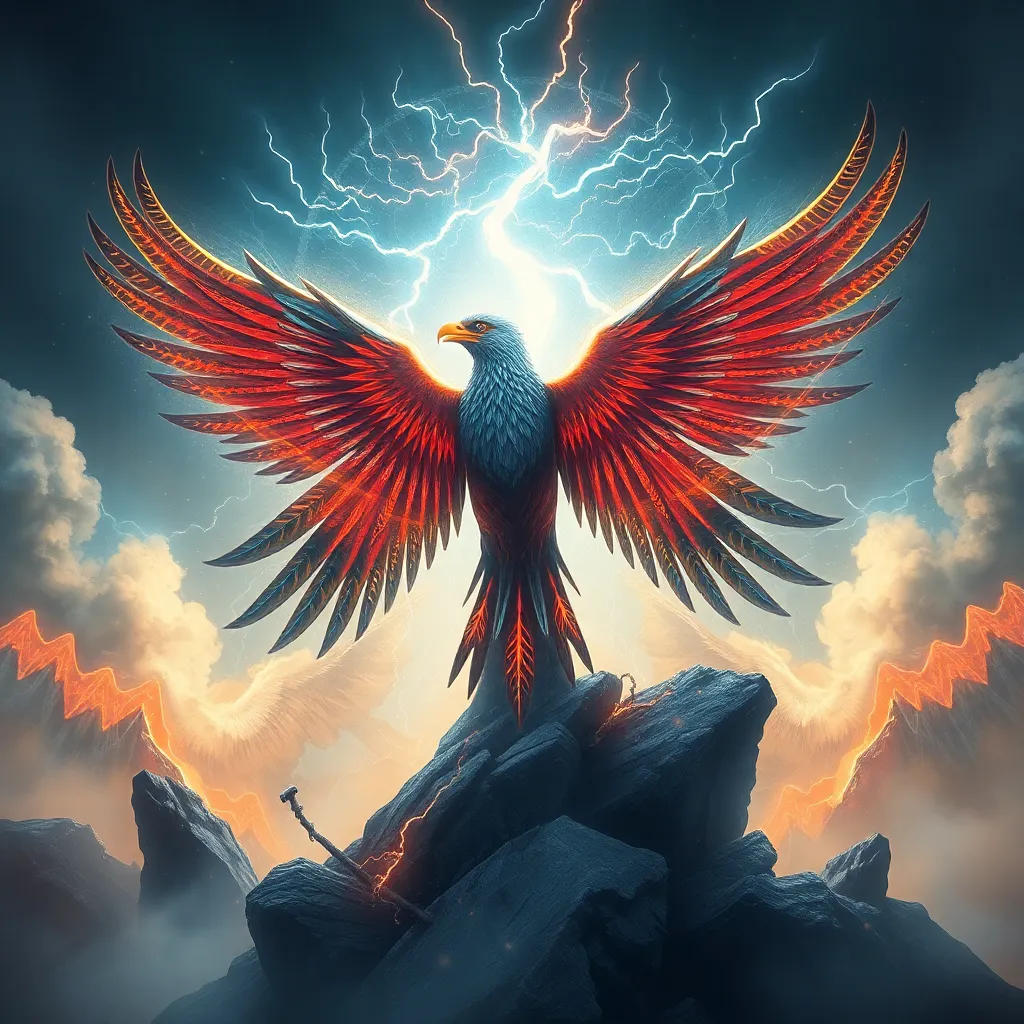
The Thunderbird is a significant figure in various Indigenous cultures of North America, embodying the essence of nature’s power and spirituality. This majestic creature is often depicted as a giant bird capable of creating thunder and storms with its wings. The Thunderbird holds a vital place in the mythology and traditions of many tribes, serving as a symbol of strength, transformation, and protection.
This article explores the rich mythology surrounding the Thunderbird, its physical characteristics, its representation in art and literature, its role as a cultural icon, and its connection to nature and environmental awareness. Additionally, we will discuss the challenges faced in preserving the Thunderbird’s significance in contemporary society.
II. The Mythological Origins of the Thunderbird
The Thunderbird’s mythology varies across different Indigenous tribes, each with their own unique stories and interpretations.
A. Indigenous American beliefs and stories
In many Indigenous cultures, the Thunderbird is revered as a powerful spirit and a connection to the divine. It is often associated with rain, fertility, and the nurturing aspects of nature. Tribes such as the Ojibwe, Lakota, and Zuni have rich narratives that depict the Thunderbird as a creator deity.
B. Variations in Thunderbird mythology across different tribes
Each tribe’s story brings unique elements to the Thunderbird’s character:
- Ojibwe: The Thunderbird is seen as a protector of the people, often battling water spirits to ensure safe travels.
- Lakota: The Thunderbird is a symbol of power, believed to bring storms and control the weather.
- Zuni: The Zuni people view the Thunderbird as a vital force in agricultural success, as it brings rain to nourish the crops.
C. The Thunderbird as a creator and protector
Many narratives position the Thunderbird as a guardian figure, using its immense power to protect the earth and its inhabitants from malevolent forces. This dual role as both creator and protector emphasizes its importance in maintaining balance in nature.
III. Physical Characteristics and Symbolism
Descriptions of the Thunderbird in folklore are as varied as the tribes that celebrate it. However, certain characteristics are commonly attributed to this mythical creature.
A. Descriptions of the Thunderbird in folklore
The Thunderbird is often depicted as an enormous bird, with wings that span wide enough to create thunderous sounds. Its feathers are frequently described as vibrant and powerful, embodying the colors of the storm.
B. The association with storms, lightning, and thunder
Thunderbird mythology is deeply intertwined with natural phenomena. The bird’s flapping wings are said to cause thunder, while its eyes are believed to flash with lightning. This connection to storms symbolizes the Thunderbird’s control over natural forces.
C. Symbolism of strength, power, and transformation
The Thunderbird represents not only physical strength but also spiritual transformation. It embodies the idea that through challenges, one can emerge stronger and more powerful. This transformative symbolism resonates with many aspects of Indigenous cultural beliefs.
IV. The Thunderbird in Art and Literature
The Thunderbird has inspired countless artistic expressions throughout history, reflecting its significance in Indigenous cultures.
A. Representation in traditional Native American art
Traditional art often features the Thunderbird in various forms, including totem poles, pottery, and woven textiles. These artistic representations serve as a connection to cultural identity and storytelling.
B. The Thunderbird in modern literature and popular culture
In contemporary literature and media, the Thunderbird continues to be a powerful symbol. It appears in novels, films, and graphic novels, often representing themes of strength and resilience.
C. Analysis of artistic interpretations and their meanings
Modern interpretations of the Thunderbird often explore its role as a guardian and a symbol of power. Artists use the image of the Thunderbird to comment on environmental issues, cultural preservation, and identity.
V. The Thunderbird as a Cultural Icon
The Thunderbird plays a vital role in the cultural identity of many Indigenous tribes.
A. The role of the Thunderbird in tribal identity
For many tribes, the Thunderbird is a central figure in their mythology and worldview. It serves as a reminder of their connection to nature and the spiritual world.
B. Contemporary use of the Thunderbird in branding and symbolism
In modern society, the Thunderbird has been adopted in various forms of branding, including sports teams and businesses. This appropriation often raises questions about cultural sensitivity and the importance of respecting Indigenous symbols.
C. The impact of the Thunderbird on environmental awareness
The Thunderbird’s association with nature and storms can be a powerful symbol for environmental movements, reminding us of the need to respect and protect our natural world.
VI. The Thunderbird and Nature’s Power
The Thunderbird serves as a vital representation of natural forces and ecological balance.
A. How the Thunderbird represents natural forces
The Thunderbird is an embodiment of the raw power of nature, representing the storms that can both create and destroy. It symbolizes the interconnectedness of all living things and the importance of maintaining balance.
B. The connection between the Thunderbird and ecological balance
In many Indigenous belief systems, the Thunderbird is seen as a mediator between the earth and the heavens, reinforcing the idea that all elements of nature must work together in harmony.
C. Lessons from Thunderbird mythology for modern environmentalism
The stories of the Thunderbird teach us valuable lessons about stewardship, respect for nature, and the importance of protecting our environment for future generations.
VII. Challenges in Preserving Thunderbird Traditions
Despite its significance, the Thunderbird and its associated traditions face numerous challenges in the modern world.
A. The impact of modernization on Indigenous cultures
As societies modernize, traditional narratives and practices can be at risk of being forgotten or altered. This loss threatens the cultural heritage of Indigenous peoples.
B. Efforts to revitalize and maintain Thunderbird narratives
Many Indigenous communities are actively working to revitalize their cultural traditions, including the stories of the Thunderbird, through educational programs, workshops, and community events.
C. Importance of education and advocacy in cultural preservation
Education about Indigenous cultures and their symbols is crucial for fostering respect and understanding. Advocacy for cultural preservation efforts can help ensure that the stories of the Thunderbird continue to be shared and honored.
VIII. Conclusion
The Thunderbird stands as a potent symbol of nature’s power, embodying the strength, resilience, and transformative potential of the natural world. Its significance spans across various Indigenous cultures, reflecting deep spiritual beliefs and connections to the earth.
As we navigate contemporary challenges, the legacy of the Thunderbird reminds us of the importance of respecting and appreciating Indigenous cultures and their rich narratives. It calls us to understand the profound lessons embedded in their stories and to work towards a more harmonious relationship with nature.
In honoring the Thunderbird, we embrace a commitment to cultural preservation and environmental stewardship, ensuring that the powerful symbols of our past continue to resonate in our future.