The Winged Stallion of the Greeks: A Deep Dive into Pegasus Mythology
I. Introduction to Pegasus
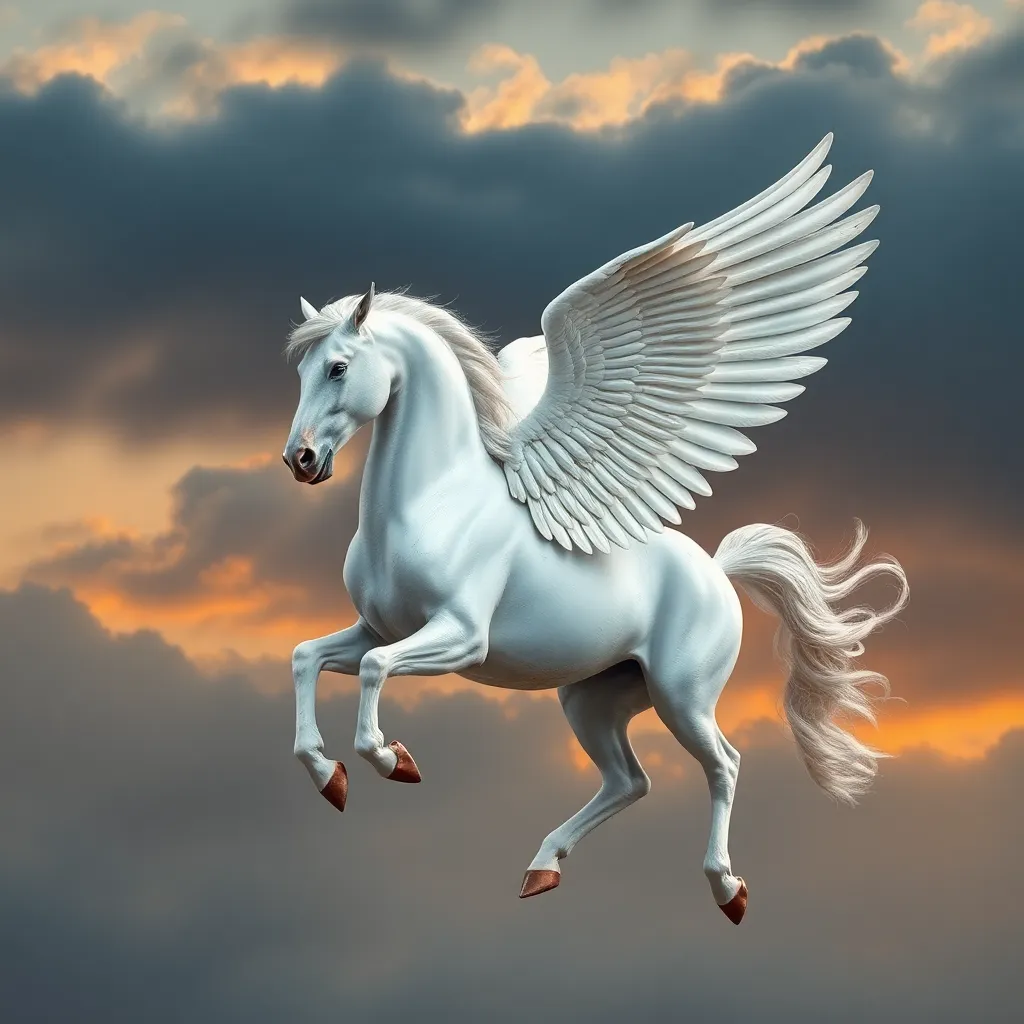
In the realm of Greek mythology, few figures capture the imagination quite like Pegasus, the majestic winged horse. Pegasus symbolizes not only beauty and grace but also the heroic ideals of ancient Greece. His stories are woven into the fabric of Greek mythology, offering insights into the values and beliefs of the time.
This article aims to explore the origins, significance, and enduring legacy of Pegasus. From his birth to his celestial journey, we will delve into the rich tapestry of myths and cultural interpretations surrounding this iconic creature.
II. Origins of Pegasus
A. Birth of Pegasus from Medusa’s blood
Pegasus’s origins are as dramatic as his character. According to myth, he was born from the blood of Medusa, the Gorgon, when she was slain by the hero Perseus. As Perseus cut off Medusa’s head, Pegasus and his brother Chrysaor emerged from her neck, symbolizing the duality of beauty and horror.
B. Connection to the Gorgon myth and its implications
The birth of Pegasus from Medusa’s blood is significant as it intertwines the themes of transformation and duality. Medusa, once a beautiful maiden, became a monster cursed by Athena. Pegasus serves as a reminder of the complexities of beauty and the consequences of divine wrath.
C. Exploration of Pegasus’s lineage and parentage
Beyond his immediate lineage, Pegasus is considered a descendant of the primordial deities. His lineage connects him to the Titans and the gods, reinforcing his status as a creature of divine origin. This connection enhances his role in various myths, where he often assists heroes in their quests.
III. The Iconography of Pegasus
A. Artistic representations through history
Throughout history, Pegasus has been a favored subject in art, from ancient pottery to Renaissance paintings. Artists depicted him in various forms, often highlighting his majestic wings and graceful form.
B. Symbolism of wings and flight in Greek art
The wings of Pegasus symbolize freedom and transcendence. In Greek art, they often represent the aspiration to rise above earthly struggles and achieve greatness. This symbolism resonates deeply within the context of Greek values, emphasizing heroism and divine favor.
C. Variations in depictions across different regions and time periods
- Classical Period: Pegasus is often shown in battle scenes, emphasizing his role as a warrior companion.
- Hellenistic Art: Focus shifts to more decorative representations, showcasing elegance and beauty.
- Renaissance: Artists like Leonardo da Vinci imbue Pegasus with a sense of divine inspiration and creativity.
IV. Tales of Pegasus in Greek Mythology
A. The role of Pegasus in the adventures of Bellerophon
One of the most famous tales involving Pegasus is his partnership with the hero Bellerophon. Bellerophon, seeking to prove his worth, tamed Pegasus with the help of a golden bridle given to him by Athena. Together, they embarked on numerous adventures, showcasing the bond between horse and rider.
B. Key myths involving Pegasus, including the Chimera slaying
Among their most notable exploits was the defeat of the Chimera, a fearsome creature with the body of a lion, the head of a goat, and a tail that ended in a snake. Bellerophon, riding Pegasus, soared above the monster, launching arrows from the sky and ultimately slaying it. This myth not only highlights their bravery but also reinforces the idea of the hero’s journey.
C. The significance of Pegasus’s partnership with heroes
Pegasus’s partnership with heroes symbolizes the union of strength and wisdom. His ability to fly represents the height of aspiration, while Bellerophon’s earthly struggles signify the trials that heroes must overcome. Together, they embody the harmony between the mortal and the divine.
V. Pegasus in Ancient Literature
A. Analysis of references in classical texts (e.g., Hesiod, Pindar)
Pegasus appears in various classical texts, notably in the works of Hesiod and Pindar. Hesiod describes his birth and divine nature, while Pindar emphasizes his role as a source of inspiration for poets and artists. These references illustrate Pegasus’s multifaceted character, shifting from a mere creature to a symbol of artistic inspiration.
B. The evolution of Pegasus’s character through literature
As literature evolved, so did the portrayal of Pegasus. From a heroic steed to a symbol of poetic inspiration, Pegasus’s character reflected the changing values and artistic movements of different eras. His journey through literature showcases the ability of myth to adapt and resonate with new generations.
C. Depictions in later works and their cultural impact
Later works, including those of the Romantic period, saw Pegasus associated with the ideals of freedom and creativity. Poets and artists frequently invoked his image as a metaphor for the lofty aspirations of the human spirit, demonstrating the lasting impact of Pegasus on cultural expressions.
VI. Pegasus and the Stars: The Constellation
A. The mythological journey of Pegasus to the heavens
Pegasus’s story does not end on earth; he ascends to the heavens after his death. The gods honored him by placing him among the stars, forming the constellation Pegasus. This transition from earthly hero to celestial being symbolizes the eternal nature of myth and legacy.
B. Explanation of the Pegasus constellation and its significance
The Pegasus constellation is prominent in the night sky, characterized by its distinctive square shape. It serves as a navigational guide for travelers and a source of inspiration for stargazers. The constellation represents the idea of reaching for the stars and the pursuit of dreams.
C. The influence of celestial imagery on the myth
The celestial imagery associated with Pegasus emphasizes themes of immortality and transcendence. The connection between Pegasus and the stars illustrates the ancient Greeks’ fascination with the cosmos, reflecting their belief in the divine influence on human lives.
VII. Modern Interpretations and Cultural Impact
A. Pegasus in contemporary literature, film, and art
In modern culture, Pegasus continues to inspire. He appears in various forms of literature, film, and art, often embodying the themes of creativity and freedom. From Disney’s animated features to fantasy novels, Pegasus remains a beloved symbol.
B. Symbolism of Pegasus in modern contexts (freedom, creativity)
Today, Pegasus represents freedom and the boundless potential of the human spirit. Artists and writers use his image to convey messages of inspiration, encouraging individuals to pursue their dreams and embrace their creative impulses.
C. The enduring legacy of Pegasus in popular culture
- Literature: Featured in young adult novels and fantasy series.
- Film: Appears in animated and live-action films, often as a symbol of hope.
- Art: Continues to inspire modern artists, blending classical themes with contemporary styles.
VIII. Conclusion
Pegasus holds a significant place in mythology and culture, embodying ideals of heroism, beauty, and artistic inspiration. His story resonates across centuries, reflecting the timeless appeal of myth and its ability to adapt to changing cultural landscapes.
As we reflect on the legacy of Pegasus, we are reminded of the enduring power of stories to inspire and uplift the human spirit. The tale of the winged stallion continues to be relevant today, serving as a beacon of creativity and aspiration for all who dare to dream.